Tamil Technicians – C Programming Course · Mini Project & Practice
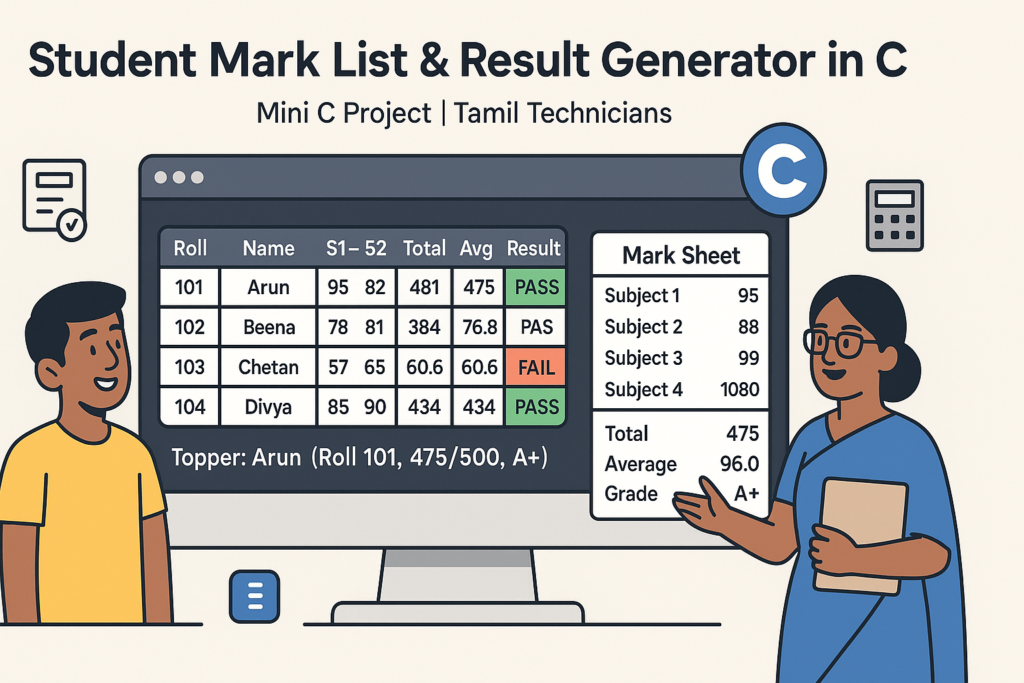
Mini C Project – Student Mark List & Result Generator in C (Console Project)
A Student Mark List & Result Generator is one of the most popular mini projects in C. It is simple enough for beginners, but powerful enough to cover real-world concepts: arrays, structures, loops, functions, conditionals and even file handling.
In this detailed tutorial, we’ll design and implement a console-based C mini project that:
- Stores details of multiple students (roll number, name, marks in multiple subjects).
- Calculates total marks, average and grade for each student.
- Determines pass/fail status based on subject-wise and overall criteria.
- Displays a neat mark sheet and class summary in the terminal.
- Optionally saves results to a text file for future reference.
1. Project Overview – What We Are Building
Imagine you are a teacher or lab in-charge. For each class, you want to quickly enter student marks and generate:
- An individual mark sheet (roll number, name, subject marks, total, average, grade).
- A class summary: number of students passed, failed, and class topper.
Student Details
Number of students, roll number, name, subject marks for each student.
Results
Calculate total, average, grade, pass/fail, and find class topper.
Mark Sheet
Print formatted mark list per student and overall class summary on the console.
File Save
Save student results to a text file for later viewing or printing.
This mini project will consolidate your understanding of:
- Arrays – storing marks for each subject and multiple students.
- Structures – grouping related data for each student.
- Functions – for calculating grades, printing mark sheets, saving to file.
- Loops & conditionals – for iterating over students and applying pass/fail rules.
- File handling – optional step for writing results to disk.
2. Requirements & Assumptions
Before we design the program, we define a few assumptions to keep things clean:
- We will handle up to 50 students in a class.
- Each student has marks in 5 subjects (e.g., Tamil, English, Maths, Science, Computer).
- Marks are out of 100 for each subject.
- Passing criteria:
- Each subject mark must be >= 35.
- OR you can modify this threshold easily later.
- Grade rules (you can customize):
- A+ for average ≥ 90
- A for average ≥ 80
- B for average ≥ 70
- C for average ≥ 60
- D for average ≥ 50
- F for average < 50 or any subject failed
3. Designing Data Structures – struct Student
To represent a student, we need multiple pieces of information grouped together. In C, the best tool for
this is a struct.
3.1 Student structure fields
- rollNo – integer.
- name – string (array of chars).
- marks[5] – array of integers, one per subject.
- total – integer or float (sum of marks).
- average – float.
- grade – character (A+, A, B, etc.; we can use a string or just a char).
- result – string like “PASS” or “FAIL”.
#define MAX_SUBJECTS 5
typedef struct {
int rollNo;
char name[50];
int marks[MAX_SUBJECTS];
int total;
float average;
char grade[3]; // e.g., "A+", "B", "F"
char result[10]; // "PASS" or "FAIL"
} Student;
For the entire class, we will have an array of Student:
#define MAX_STUDENTS 50
Student students[MAX_STUDENTS];
int studentCount;4. Designing the Program Flow
It’s always better to think about the overall flow before writing code. Here is a simple step-by-step plan:
- Display a welcome heading for the result generator.
- Ask how many students (
studentCount). - For each student:
- Read roll number and name.
- Read marks for each subject.
- Compute total, average.
- Determine grade and pass/fail result.
- After data entry:
- Print a formatted mark list for the whole class (table view).
- Print a detailed mark sheet for each student (optional).
- Find and display class topper (highest total or average).
- Show number of students passed and failed.
- Ask user if they want to save results to file.
- Exit the program.
We can break the logic into reusable functions:
void inputStudentData(Student *s, int rollIndex)void calculateResult(Student *s)void printClassTable(Student s[], int n)void printStudentDetail(const Student *s)int findTopperIndex(Student s[], int n)void saveResultsToFile(Student s[], int n, const char *filename)
5. Result & Grade Logic
We separate the calculation logic into a function that:
- Computes total and average.
- Checks if any subject is below the pass mark (e.g., 35).
- Assigns a grade based on average (if passed in all subjects).
- Sets the result string to “PASS” or “FAIL”.
#define PASS_MARK 35
void calculateResult(Student *s) {
int i;
int failed = 0;
s->total = 0;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SUBJECTS; i++) {
s->total += s->marks[i];
if (s->marks[i] < PASS_MARK) {
failed = 1;
}
}
s->average = s->total / (float)MAX_SUBJECTS;
if (failed) {
strcpy(s->grade, "F");
strcpy(s->result, "FAIL");
return;
}
if (s->average >= 90) {
strcpy(s->grade, "A+");
} else if (s->average >= 80) {
strcpy(s->grade, "A");
} else if (s->average >= 70) {
strcpy(s->grade, "B");
} else if (s->average >= 60) {
strcpy(s->grade, "C");
} else if (s->average >= 50) {
strcpy(s->grade, "D");
} else {
strcpy(s->grade, "F");
failed = 1;
}
if (failed) {
strcpy(s->result, "FAIL");
} else {
strcpy(s->result, "PASS");
}
}6. Full Code – Student Mark List & Result Generator (Console)
Below is a complete C program that:
- Reads multiple students’ marks.
- Calculates total, average, grade and result.
- Prints a class-wise mark list table and topper information.
- Optionally saves data to a text file.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_STUDENTS 50
#define MAX_SUBJECTS 5
#define PASS_MARK 35
typedef struct {
int rollNo;
char name[50];
int marks[MAX_SUBJECTS];
int total;
float average;
char grade[3]; // "A+", "B", "C", "F"
char result[10]; // "PASS" or "FAIL"
} Student;
void inputStudentData(Student *s, int index) {
int i;
printf("\\n---- Enter details for student %d ----\\n", index + 1);
printf("Roll number: ");
scanf("%d", &s->rollNo);
printf("Name: ");
scanf(" %49[^\n]", s->name);
printf("Enter marks for %d subjects (out of 100):\\n", MAX_SUBJECTS);
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SUBJECTS; i++) {
printf("Subject %d: ", i + 1);
scanf("%d", &s->marks[i]);
if (s->marks[i] < 0) {
s->marks[i] = 0;
} else if (s->marks[i] > 100) {
s->marks[i] = 100;
}
}
}
void calculateResult(Student *s) {
int i;
int failed = 0;
s->total = 0;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SUBJECTS; i++) {
s->total += s->marks[i];
if (s->marks[i] < PASS_MARK) {
failed = 1;
}
}
s->average = s->total / (float)MAX_SUBJECTS;
if (failed) {
strcpy(s->grade, "F");
strcpy(s->result, "FAIL");
return;
}
if (s->average >= 90) {
strcpy(s->grade, "A+");
} else if (s->average >= 80) {
strcpy(s->grade, "A");
} else if (s->average >= 70) {
strcpy(s->grade, "B");
} else if (s->average >= 60) {
strcpy(s->grade, "C");
} else if (s->average >= 50) {
strcpy(s->grade, "D");
} else {
strcpy(s->grade, "F");
failed = 1;
}
if (failed) {
strcpy(s->result, "FAIL");
} else {
strcpy(s->result, "PASS");
}
}
void printClassTable(Student s[], int n) {
int i, j;
printf("\\n===============================================================\\n");
printf(" STUDENT MARK LIST - CLASS SUMMARY \\n");
printf("===============================================================\\n");
printf("%-6s %-20s ", "Roll", "Name");
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SUBJECTS; i++) {
printf("S%-2d ", i + 1);
}
printf(" Total Avg Gr Result\\n");
printf("---------------------------------------------------------------\\n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%-6d %-20s ", s[i].rollNo, s[i].name);
for (j = 0; j < MAX_SUBJECTS; j++) {
printf("%-4d ", s[i].marks[j]);
}
printf("%-6d %-5.1f %-3s %-6s\\n",
s[i].total, s[i].average, s[i].grade, s[i].result);
}
printf("===============================================================\\n");
}
void printStudentDetail(const Student *s) {
int i;
printf("\\n---------------- STUDENT RESULT ----------------\\n");
printf("Roll No : %d\\n", s->rollNo);
printf("Name : %s\\n", s->name);
printf("------------------------------------------------\\n");
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SUBJECTS; i++) {
printf("Subject %d: %d\\n", i + 1, s->marks[i]);
}
printf("------------------------------------------------\\n");
printf("Total : %d\\n", s->total);
printf("Average : %.2f\\n", s->average);
printf("Grade : %s\\n", s->grade);
printf("Result : %s\\n", s->result);
printf("------------------------------------------------\\n");
}
int findTopperIndex(Student s[], int n) {
int i, topperIndex = 0;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (s[i].total > s[topperIndex].total) {
topperIndex = i;
}
}
return topperIndex;
}
void saveResultsToFile(Student s[], int n, const char *filename) {
int i, j;
FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "w");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("Error: Could not open %s for writing.\\n", filename);
return;
}
fprintf(fp, "STUDENT MARK LIST & RESULT SHEET\\n\\n");
fprintf(fp, "%-6s %-20s ", "Roll", "Name");
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SUBJECTS; i++) {
fprintf(fp, "S%-2d ", i + 1);
}
fprintf(fp, " Total Avg Gr Result\\n");
fprintf(fp, "---------------------------------------------------------------\\n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fprintf(fp, "%-6d %-20s ", s[i].rollNo, s[i].name);
for (j = 0; j < MAX_SUBJECTS; j++) {
fprintf(fp, "%-4d ", s[i].marks[j]);
}
fprintf(fp, "%-6d %-5.1f %-3s %-6s\\n",
s[i].total, s[i].average, s[i].grade, s[i].result);
}
fclose(fp);
printf("Results successfully saved to %s\\n", filename);
}
int main() {
Student students[MAX_STUDENTS];
int n, i;
int passCount = 0, failCount = 0;
int topperIndex;
char choice;
printf("===============================================\\n");
printf(" STUDENT MARK LIST & RESULT GENERATOR (C)\\n");
printf("===============================================\\n\\n");
printf("Enter number of students (max %d): ", MAX_STUDENTS);
scanf("%d", &n);
if (n <= 0 || n > MAX_STUDENTS) {
printf("Invalid number of students. Exiting.\\n");
return 1;
}
// Input and calculate for each student
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
inputStudentData(&students[i], i);
calculateResult(&students[i]);
}
// Count pass/fail
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (strcmp(students[i].result, "PASS") == 0) {
passCount++;
} else {
failCount++;
}
}
// Find topper
topperIndex = findTopperIndex(students, n);
// Print class table
printClassTable(students, n);
// Print class summary
printf("\\nCLASS SUMMARY:\\n");
printf("Total students : %d\\n", n);
printf("Passed : %d\\n", passCount);
printf("Failed : %d\\n", failCount);
printf("Topper : %s (Roll %d, Total %d, Avg %.2f, Grade %s)\\n",
students[topperIndex].name,
students[topperIndex].rollNo,
students[topperIndex].total,
students[topperIndex].average,
students[topperIndex].grade);
// Optionally print detail for one student
printf("\\nDo you want to see detail of a student? (y/n): ");
scanf(" %c", &choice);
if (choice == 'y' || choice == 'Y') {
int roll;
printf("Enter roll number to view detail: ");
scanf("%d", &roll);
int found = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (students[i].rollNo == roll) {
printStudentDetail(&students[i]);
found = 1;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
printf("No student found with roll number %d.\\n", roll);
}
}
// Optionally save results to file
printf("\\nDo you want to save the results to a file? (y/n): ");
scanf(" %c", &choice);
if (choice == 'y' || choice == 'Y') {
saveResultsToFile(students, n, "results.txt");
}
printf("\\nProgram ended. Goodbye!\\n");
return 0;
}gcc student_result.c -o student_result
Run with: ./student_result (Linux/macOS) or student_result.exe (Windows).
7. Testing the Mini Project – Sample Scenario
Let’s walk through a sample test to ensure the logic works:
Example Input (3 students, 5 subjects)
- Student 1:
- Roll: 101
- Name: Arun
- Marks: 80, 75, 90, 85, 88
- Student 2:
- Roll: 102
- Name: Bala
- Marks: 60, 55, 45, 50, 58
- Student 3:
- Roll: 103
- Name: Charu
- Marks: 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 (note: first subject is below pass mark)
The program should:
- Compute totals and averages correctly.
- Assign grade and result:
- Arun – high average, likely A or A+ and PASS.
- Bala – average around 53.6 (PASS, grade D).
- Charu – FAIL because of subject 1 < 35 (grade F).
- Show class summary – 2 passed, 1 failed, topper = Arun.
- All students pass.
- All students fail in at least one subject.
- Edge case: marks = 35 exactly (should pass).
- Marks input < 0 or > 100 (program clamps to 0 or 100 as written).
8. Extension Ideas – Make the Project More Powerful
Once the basic project works, you can level it up with new features:
8.1 Custom subject names
Instead of just “Subject 1, 2, 3…”, allow the user to enter subject names at the beginning:
char subjectNames[MAX_SUBJECTS][30];
int i;
printf("Enter names of %d subjects:\\n", MAX_SUBJECTS);
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SUBJECTS; i++) {
printf("Subject %d name: ", i + 1);
scanf(" %29[^\n]", subjectNames[i]);
}
Then use subjectNames[i] when printing.
8.2 Class-wise statistics
- Average marks per subject across all students.
- Highest and lowest mark per subject.
- Overall class average.
8.3 Ranking
Sort students by total or average and assign ranks.
You can use a simple bubble sort for small numbers of students.
8.4 Multiple classes or sections
Extend the program to handle multiple classes (e.g., Class 10A, 10B, 10C) using an outer loop or another structure.
8.5 Export to CSV
Instead of a free-form text file, write results in CSV format so that they can be opened directly in Excel or Google Sheets:
fprintf(fp, "Roll,Name,S1,S2,S3,S4,S5,Total,Average,Grade,Result\n");9. Learning Checklist – Student Mark List Mini Project
- I can design a
struct Studentwith roll number, name, marks and result fields. - I can store multiple students in an array and iterate through them with loops.
- I understand how to compute total and average from subject marks.
- I can implement pass/fail and grade logic using if–else conditions.
- I can format console output into a neat table (class-wise mark list).
- I can write helper functions to keep
main()clean and modular. - I can use file handling to save results to a text/CSV file.
- I can extend the mini project with features like topper, ranking and subject statistics.
FAQ: Student Mark List & Result Generator in C
1. Is this mini project suitable for first-year or diploma students?
Yes. This project is ideal for first-year engineering, diploma, B.Sc., BCA and ITI students who have
covered the basics of C (arrays, loops, if, switch). It demonstrates a realistic
use case and can be shown in labs and internal assessments.
2. Do I need pointers and dynamic memory for this project?
No. The basic version uses static arrays and structures. You don’t need dynamic memory
(malloc()) to complete it. However, if you later want to support a very large number of students,
you can convert the arrays to dynamically allocated memory as an advanced exercise.
3. Can I customize the number of subjects and passing criteria?
Absolutely. Just change MAX_SUBJECTS, update the marks input loop and modify
PASS_MARK or the grade boundaries in calculateResult(). The structure of the code
makes such changes straightforward.
4. How can I present this project in my viva or lab exam?
Prepare a short explanation of the problem statement, show your data structures (the Student
struct), walk through the logic for calculating total, average and grade, and then run the program with
sample input. Highlight any extensions you’ve implemented, such as file saving, topper calculation
or ranking. This shows both coding and design understanding.
Buy link ;
Contact link ;
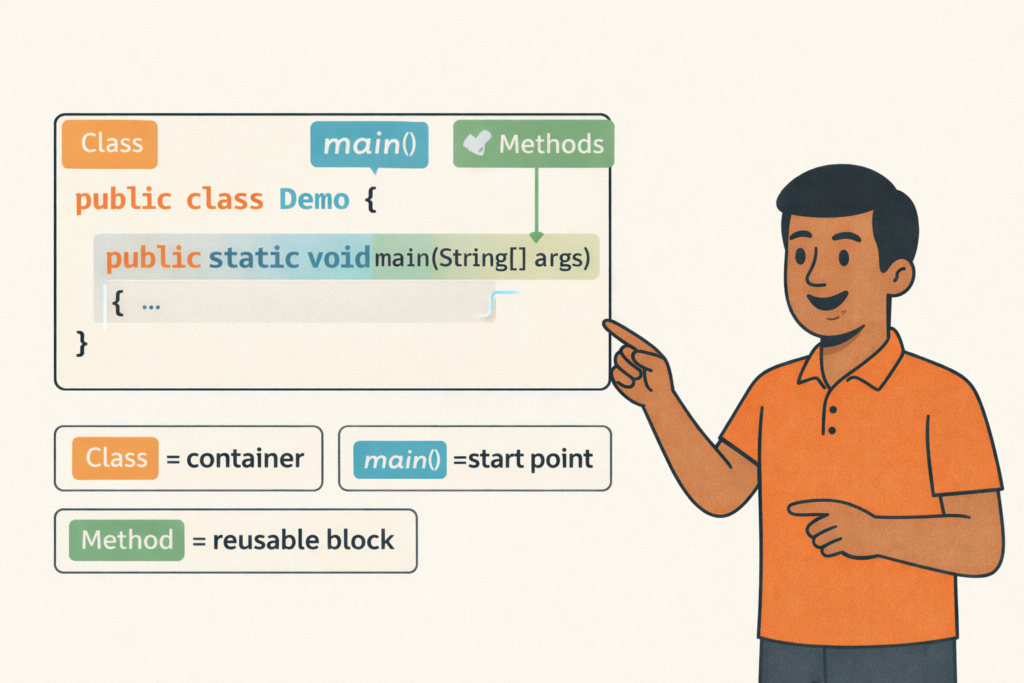
Java Program Structure (Class, main, Methods)– Full Beginner Explanation
Java Program Structure (Class, main, Methods) – Beginner Guide | Tamil Technicians TT Tamil Technicians…
Install JDK + VS Code/IntelliJ Setup+ Your First Java Program (Windows)
Install JDK + VS Code/IntelliJ Setup + First Java Program (Windows) | Tamil Technicians TT…
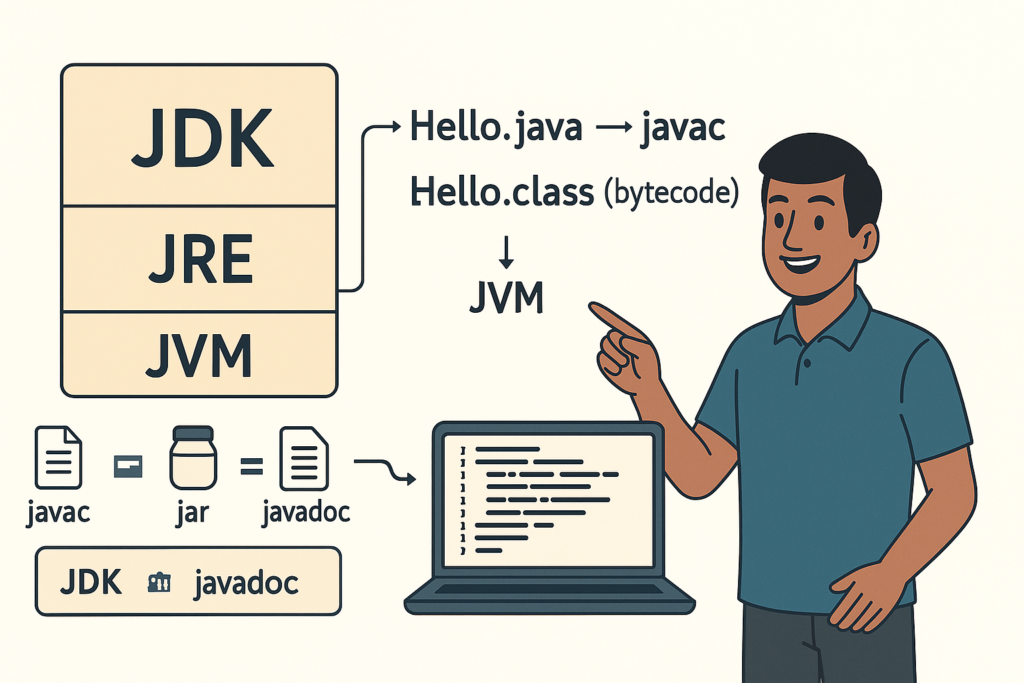
JDK vs JRE vs JVM – Easy Explanation(Compile & Run Flow for Beginners)
JDK vs JRE vs JVM – Easy Explanation (Beginner Guide) | Tamil Technicians TT Tamil…
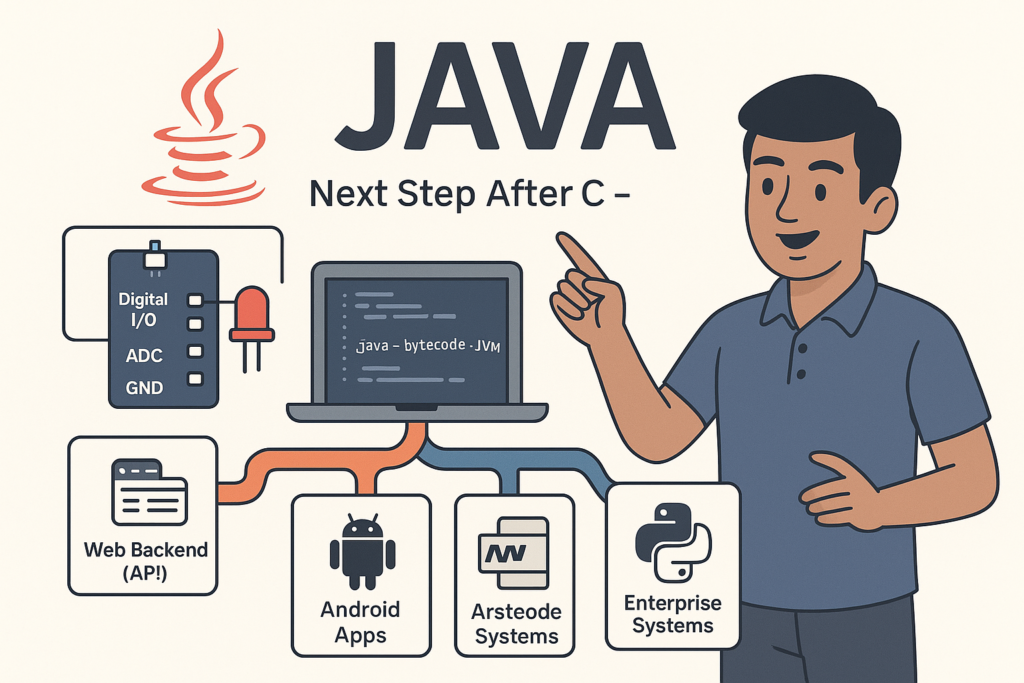
Java Introduction & Where Java is Used(Apps, Web, Banking, Android)
Java Introduction & Where Java is Used (Apps, Web, Banking, Android) | Tamil Technicians TT…
Next Step After C – What to Learn? (Embedded C, C++, Python, Linux Programming)
Next Step After C – What to Learn? (Embedded C, C++, Python, Linux Programming) |…
C for Electronics & Technicians – Basic Concepts for Embedded C
C for Electronics & Technicians – Basic Concepts for Embedded C | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
Mini C Project – Student Mark List & Result Generator in C (Console Project)
Mini C Project – Student Mark List & Result Generator in C (Console Project) |…
Mini C Projects – Simple Billing System & Calculator in C (Console Projects)
Mini C Projects – Simple Billing System & Calculator in C (Console Projects) | Tamil…
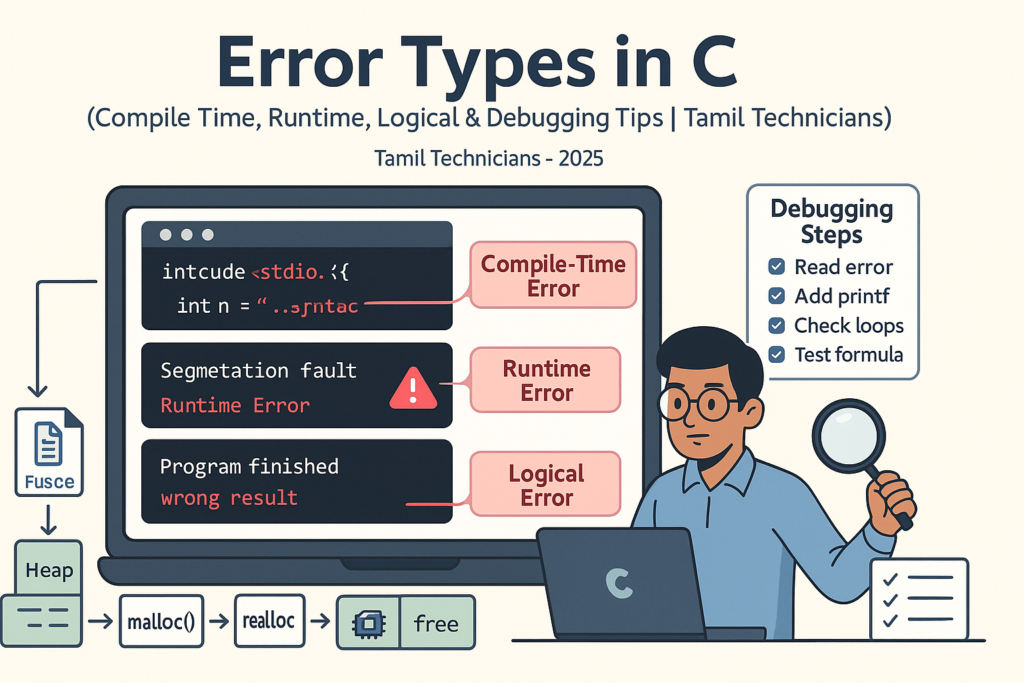
Error Types in C – Compile Time, Runtime, Logical Errors & Debugging Tips 2025
Error Types in C – Compile Time, Runtime, Logical Errors & Debugging Tips | Tamil…
Preprocessor & Macros in C – #include, #define, Conditional Compilation
Preprocessor & Macros in C – #include, #define, Conditional Compilation | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
Dynamic Memory Allocation – malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), free() Basics
Dynamic Memory Allocation in C – malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), free() Basics | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
File Handling in C – Read/Write Text Files (Sensor Log, Billing Data Examples) 2025
File Handling in C – Read/Write Text Files (Sensor Log, Billing Data Examples) | Tamil…
Storage Classes in C – auto, static, extern, register (Lifetime & Scope)
Storage Classes in C – auto, static, extern, register (Lifetime & Scope) | Tamil Technicians…
Structures in C – Struct with Examples (Student, Product, Device Data)
Structures in C – Struct with Examples (Student, Product, Device Data) | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
Pointers with Arrays, Strings & Functions – Real Use Cases
Pointers with Arrays, Strings & Functions – Real Use Cases | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
Pointers in C – Step-by-Step Visual Explanation for Beginners
Pointers in C – Step-by-Step Visual Explanation for Beginners | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians –…
Call by Value vs Call by Reference – Simple Pointer Examples in Tamil
Call by Value vs Call by Reference – Simple Pointer Examples in Tamil | Tamil…
Functions in C – User Defined Functions, Arguments, Return Types
Functions in C – User Defined Functions, Arguments, Return Types | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
Unions & Enums in C – Where and Why to Use Them?
Unions & Enums in C – Where and Why to Use Them? | Tamil Technicians…
Strings in C – char Array, gets(), puts(), String Functions (strlen, strcpy, etc.)
Strings in C – char Array, gets(), puts(), String Functions (strlen, strcpy, etc.) | Tamil…
2D Arrays in C – Tables, Matrices & Small Mini-Projects
2D Arrays in C – Tables, Matrices & Small Mini-Projects | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
Arrays in C – 1D Array Basics with Practical Examples (Marks, Bills, Readings)
Arrays in C – 1D Array Basics with Practical Examples (Marks, Bills, Readings) | Tamil…
Break, Continue & goto in C – When to Use and When to Avoid?
Break, Continue & goto in C – When to Use and When to Avoid? |…
Loops in C – for, while, do-while Complete Guide (Patterns & Practice)
Loops in C – for, while, do-while Complete Guide (Patterns & Practice) | Tamil Technicians…
switch–case in C – Menu Programs & Real Life Examples for Technicians
switch–case in C – Menu Programs & Real Life Examples for Technicians | Tamil Technicians…
Control Statements in C – if, if-else, nested if, else-if ladder (Tamil Explanation)
Control Statements in C – if, if-else, nested if, else-if ladder (Tamil Explanation) | Tamil…
Operators in C – Arithmetic, Relational, Logical & Assignment (with Examples)
Operators in C – Arithmetic, Relational, Logical & Assignment (with Examples) | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
Input & Output in C – printf(), scanf() Step-by-Step Guide 2025
Input & Output in C – printf(), scanf() Step-by-Step Guide | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
C Variables, Data Types & Constants Explained in Simple Tamil
C Variables, Data Types & Constants Explained in Simple Tamil | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
Structure of a C Program – main(), Header Files & How Code Runs?
Structure of a C Program – main(), Header Files & How Code Runs? | Tamil…
What is Programming & Why C is Important? (C Programming in Tamil for Beginners) | Tamil Technicians
What is Programming & Why C is Important? (C Programming in Tamil for Beginners) |…
C Language Introduction & Setup Guide for Beginners 2025
C Language Course Introduction & Setup Guide (Windows, Linux, macOS) | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…