What is an Audio Amplifier? The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Powerful Sound Technology
Introduction
An audio amplifier is a crucial component in any sound system, responsible for boosting weak audio signals to drive speakers and provide high-quality sound. Whether you are setting up a home theater, repairing an old sound system, or just curious about how amplifiers work, this guide will cover everything you need to know.
In this comprehensive beginner’s guide, we will explore , how it works, the different types, its components, and its applications. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of amplifiers and their role in audio technology.
What is an Audio Amplifier?
An amplifier is an electronic device designed to increase the amplitude of an audio signal, making it powerful enough to drive speakers. Without an amplifier, the sound from sources like microphones, mobile devices, or computers would be too weak to hear properly.
How Does an Audio Amplifier Work?
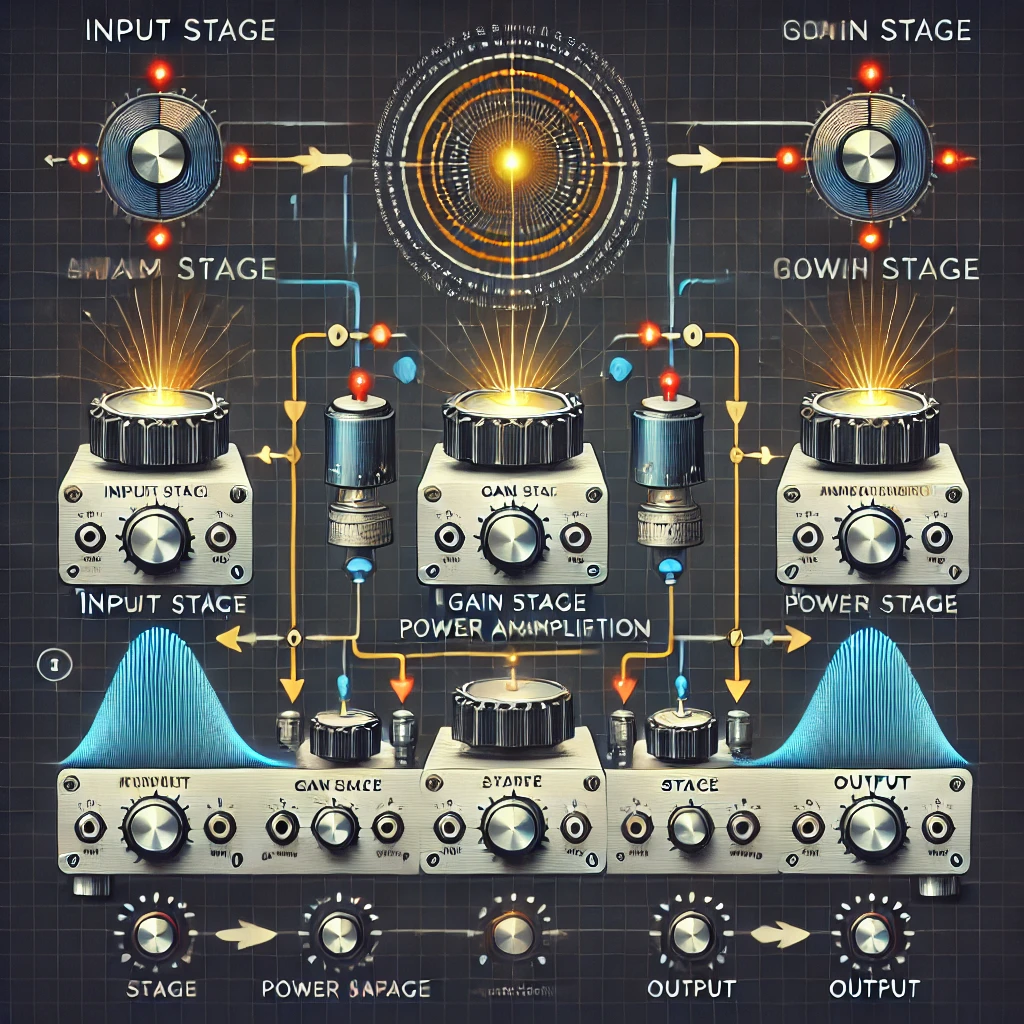
- Input Stage: The amplifier receives a weak electrical signal from an audio source (e.g., phone, microphone, CD player).
- Processing Stage: The signal passes through preamp circuits, tone controls, and gain stages to enhance and shape the sound.
- Power Amplification: The processed signal is amplified using transistors or vacuum tubes.
- Output Stage: The amplified signal is sent to the speakers, producing audible sound.
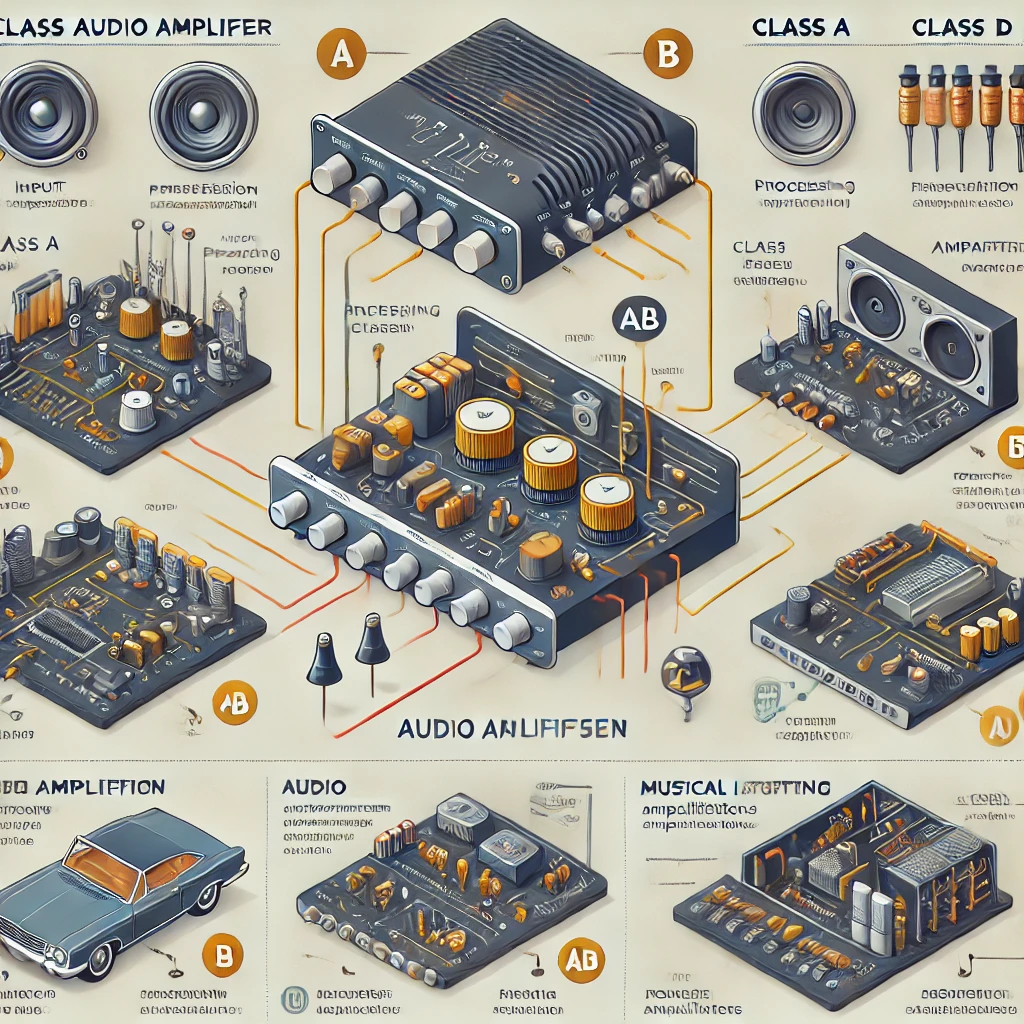
Types of Audio Amplifiers
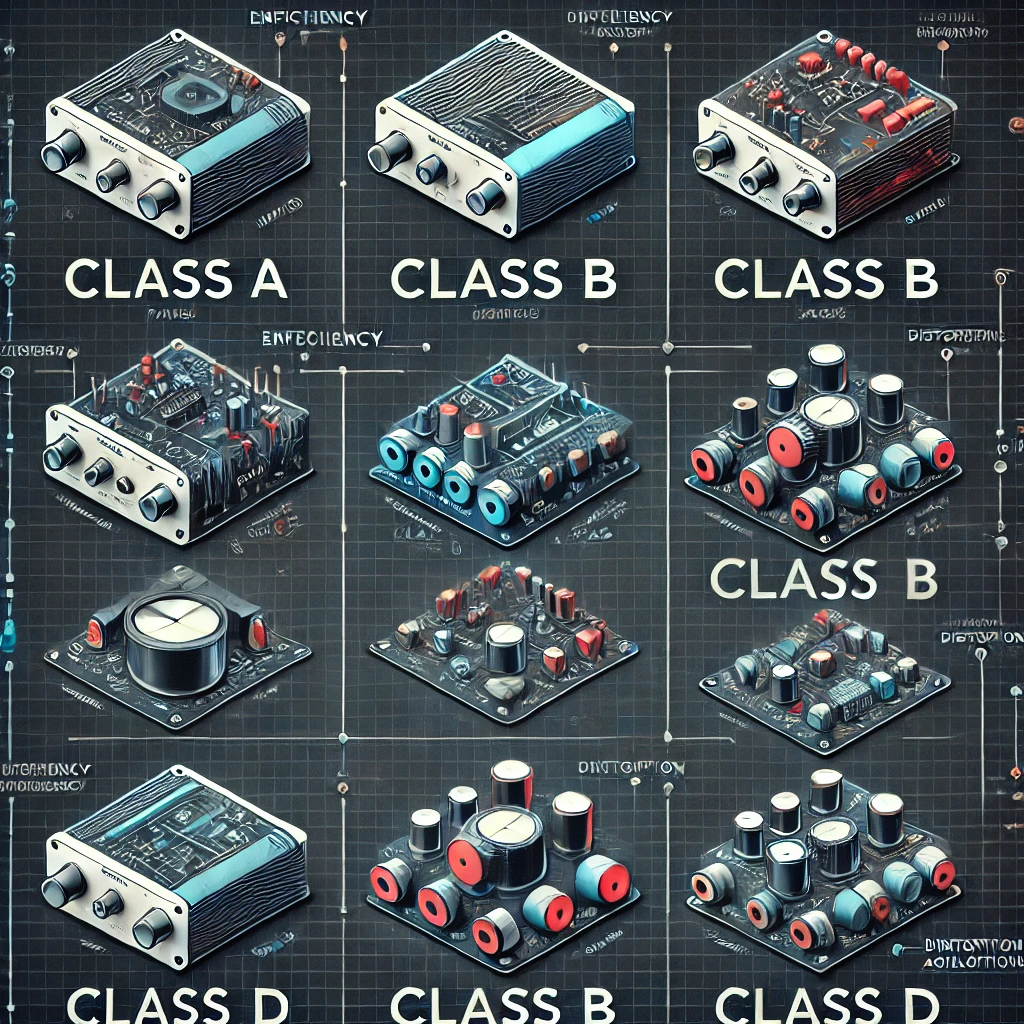

There are several types of audio amplifiers, each designed for different applications. The most common types include:
1. Class A Amplifiers
- Known for their high sound quality and low distortion.
- Operate continuously, consuming more power and generating heat.
- Used in high-end audio systems.
2. Class B Amplifiers
- More efficient than Class A, but can introduce distortion.
- Used in mid-range audio systems.
3. Class AB Amplifiers
- A hybrid of Class A and B, offering better efficiency and lower distortion.
- Commonly found in home theaters and professional audio equipment.
4. Class D Amplifiers
- Highly efficient and produce less heat.
- Often used in car audio systems, Bluetooth speakers, and portable devices.
Key Components of an Audio Amplifier
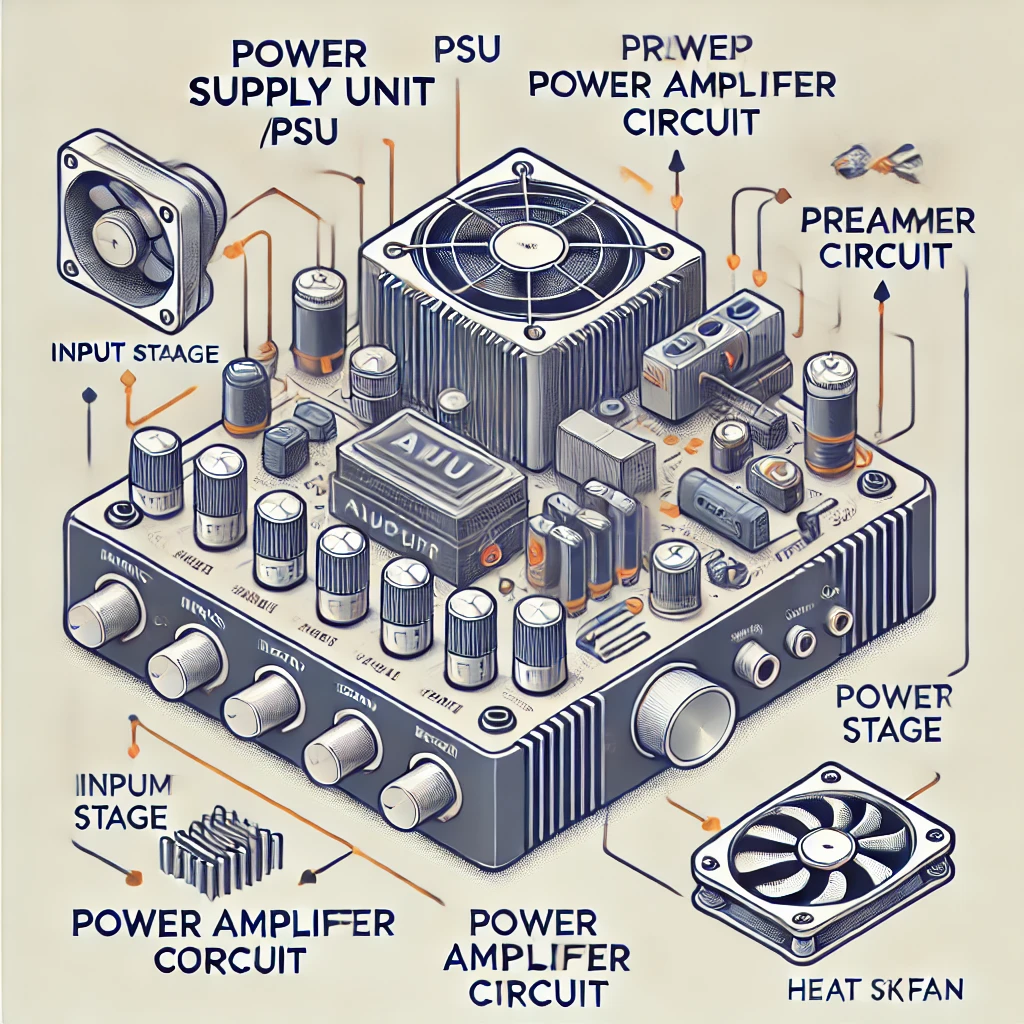
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts AC power to DC voltage needed for amplifier operation.
- Input Stage: Receives audio signals from external devices.
- Preamp Circuit: Enhances and shapes the input signal.
- Power Amplifier Circuit: Boosts the signal to drive speakers.
- Output Stage: Delivers the amplified signal to the speakers.
- Heat Sink/Fan: Helps dissipate heat generated during amplification.
Applications of Audio Amplifiers
- Home Theaters: Enhance the quality of movies and music.
- Musical Instruments: Guitar and bass amplifiers improve sound projection.
- Public Address Systems: Used in concerts, auditoriums, and large venues.
- Car Audio Systems: Improve sound clarity and power in vehicles.
- Broadcasting Stations: Essential for transmitting clear audio signals.
How to Choose the Right Audio Amplifier
When selecting an audio amplifier, consider the following factors:
1. Power Output (Wattage)
- Determines how loud your sound system can get.
- Match the amplifier wattage with your speaker’s power rating.
2. Impedance Matching
- Ensure the amplifier’s impedance matches your speaker’s impedance (e.g., 4-ohm, 8-ohm).
3. Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
- Lower THD means cleaner sound output.
- Look for amplifiers with THD below 1%.
4. Number of Channels
- Mono, stereo, or multi-channel amplifiers depending on your setup needs.
5. Additional Features
- Built-in Bluetooth, equalizers, and tone controls enhance functionality.
Common Audio Amplifier Issues and How to Fix Them
- No Sound Output: Check power connections, input sources, and speaker wiring.
- Distorted Sound: Possible causes include blown speakers, faulty capacitors, or damaged transistors.
- Overheating Issues: Ensure proper ventilation and check for faulty cooling fans or heat sinks.
- Buzzing or Humming Noise: Grounding issues, power supply problems, or damaged cables.
- One Channel Not Working: Test speaker connections and replace faulty transistors or ICs.
Internal Links (Related Articles on Our Website)
- How to Repair an Audio Amplifier: Step-by-Step Guide
- Common Audio Amplifier Problems and Solutions
- Understanding Class D Amplifiers and Their Benefits
- How Audio Amplifiers Work: A Simple Guide for Beginners.
External Links (Authoritative Sources)
Conclusion
An audio amplifier is an essential component in any sound system, amplifying weak signals to drive powerful speakers. Understanding the basics of amplifiers, their types, components, and applications will help you make informed decisions when choosing or repairing an amplifier.
If you are new to audio amplifiers, this guide provides a solid foundation. For more advanced topics, check out our in-depth guides on amplifier repair, troubleshooting, and modifications.
Images to Include:
- Diagram showing the basic working of an audio amplifier.
- Comparison of different amplifier classes (A, B, AB, D).
- Internal components of an amplifier (power supply, transistors, capacitors, etc.).
- Application examples (home theater, car audio, musical instruments).
- Troubleshooting chart for common amplifier issues.
Would you like any modifications or additional details?
Related Post’s
How to Assemble a 5.1 Amplifier Easily – Complete 2025 Guide
How to Assemble a 5.1 Amplifier Easily (2025 Full Guide) | Tamil Technicians English How…
Ultimate Guide to Power Supply for Electronics Repair & Projects
Ultimate Guide to Power Supply for Electronics Repair & Projects | Tamil Technicians Ultimate Guide…
Online Electronics Repair Training in Tamil | TAMIL TECHNICIANS
Online Electronics Repair Training in Tamil | [TAMIL TECHNICIANS] Online Electronics Repair Training in Tamil…
iPhone 17 Series – Complete Guide (Features, Price in India, Specs)
iPhone 17 Series – Complete Guide (Features, Price in India, Specs) | Tamil Technicians Home…
iPhone 17 Series – முழுமையான வழிகாட்டி (Features, Price in India, Specs)
iPhone 17 Series – முழுமையான வழிகாட்டி (Features, Price in India, Specs) | Tamil Technicians Home…
Kill Audio Hum: A Practical Guide to Star Ground & Chassis Ground
Kill Audio Hum: A Practical Guide to Star Ground & Chassis Ground TamilTechnicians • Audio…
Edge AI: Cloud இல்லாமல் Mobile & IoT Devices‑ல் Real‑Time Intelligence (2025)
Edge AI: Cloud இல்லாமல் Mobile & IoT Devices‑ல் Real‑Time Intelligence Edge AI 2025 Guide Edge…
Smartphone Dead Issue? Full Board-Level Repair Steps
Smartphone Dead Issue? Full Board-Level Repair Steps 📱 Smartphone Dead Issue? Full Board-Level Repair Steps…
Top 5 Multimeters Under ₹1000 for Beginners in India (2025) – Expert Guide
Top 5 Multimeters Under ₹1000 for Beginners (2025 Guide) Top 5 Multimeters Under ₹1000 (2025…







Pingback: 5 Key Stages: How Audio Amplifiers Work – A Powerful Guide
Pingback: 7 Proven Fixes to Instantly Fix Distorted Sound in an Audio Amplifier
Pingback: 7 Reasons Your Amplifier Overheats & Easy Fixes to Stop It (2025)