Tamil Technicians – C Programming Course · C for Electronics & Embedded Basics
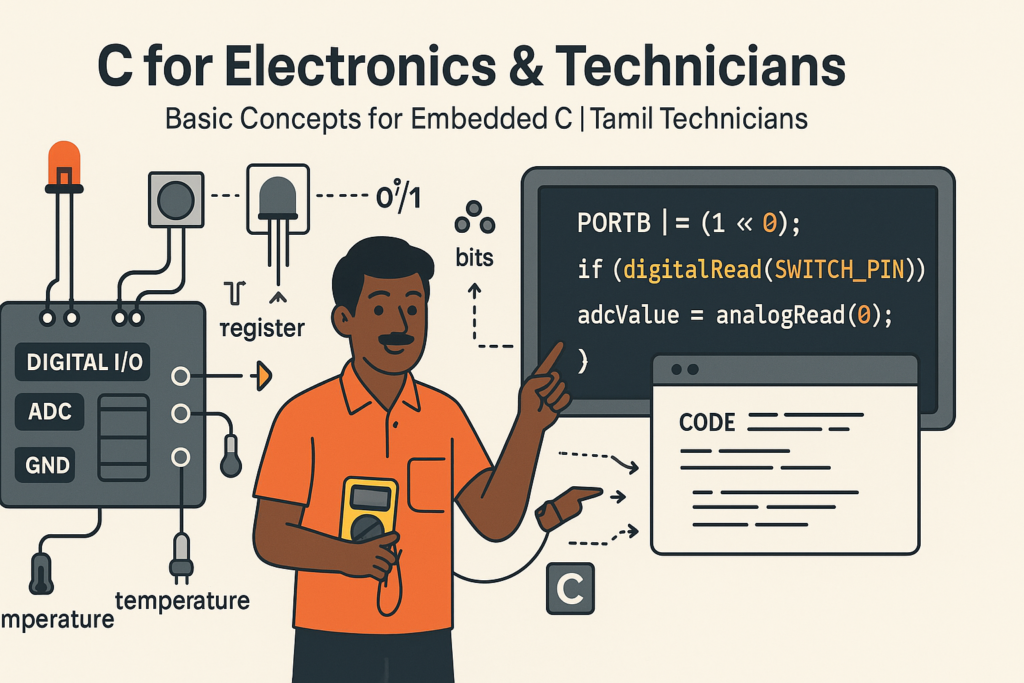
C for Electronics & Technicians – Basic Concepts for Embedded C
If you work with electronics, microcontrollers, inverters, PLC panels or embedded boards, learning C is one of the best investments you can make. Most small controllers and embedded systems are programmed in C or Embedded C.
In this lesson, we will not jump into any specific microcontroller (PIC, AVR, 8051, ARM, etc.). Instead, we’ll build a technician-friendly foundation:
- How C concepts map to real electronics: pins, voltages, inputs/outputs.
- What you must know in C before touching Embedded C on any board.
- How bits, bytes and registers relate to C variables.
- Basic ideas of digital I/O, delays, sensors and control logic in C-style pseudocode.
- Good habits that keep your embedded code safe and predictable.
1. Why C Is So Popular in Electronics & Embedded
When you open a microcontroller datasheet or firmware example, most of the time you will see code in C. There are several reasons why:
Close to Hardware
C lets you control bits, bytes and memory addresses directly. Perfect for pins, ports and registers.
Fast & Efficient
C generates compact machine code that runs fast on small microcontrollers with limited memory.
Portable
The same C logic can be moved between different controllers with only small changes to I/O parts.
Standard Language
C has decades of history, with plenty of books, tutorials, examples and tools across the world.
As an electronics technician, you already think in terms of volts, amps, pins, relays and sensors. When learning C, you simply need to add a second view: variables, bits, conditions, loops and functions. Embedded C is just the bridge between these two worlds.
2. Mapping Electronics Concepts to C Concepts
One of the best ways to learn C for embedded is to connect things you already know (hardware) with new software ideas.
| Electronics World | C / Embedded C World | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Microcontroller pin (e.g., RB0) | Bit in a register | Each pin is usually controlled by one bit in a PORT register (0 = LOW, 1 = HIGH). |
| Digital input switch | if condition on a bit |
Read pin state into C and use if (pin == 1) to check switch ON/OFF. |
| LED / relay output | Assigning to a bit | pin = 1 → LED ON, pin = 0 → LED OFF (through hardware driver). |
| ADC reading | Integer variable | ADC value (0–1023, 0–4095, etc.) stored in an int or uint16_t. |
| Timing/delay circuit | Loop or timer | Software delay loops or hardware timers controlled by C code. |
| Control logic (ladder diagram) | if, else, switch |
Branching in C is exactly like control logic blocks on paper. |
3. C Basics You Must Know Before Embedded
Before touching any microcontroller-specific registers, make sure you are comfortable with these core C topics:
Data Types
int, char, float, and unsigned types like unsigned int.
Control Statements
if, if-else, switch, for, while, do-while.
Operators
Arithmetic, relational, logical AND/OR, and especially bitwise operators.
Functions & Arrays
Breaking code into functions and handling small arrays of data (e.g., multiple readings).
4. Bits, Bytes & Registers – C View of Hardware
Inside a microcontroller, most hardware control is done through registers – special memory locations. Each register is made of bits. C gives us tools to work with these bits.
4.1 Byte, bits and hexadecimal
A typical I/O port (e.g., PORTB) might be 8 bits:
Bit: 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
| | | | | | | |
RB7 ... RB0In C you treat this as an 8-bit or 16-bit integer and use bitwise operators:
unsigned char portB; // 8-bit register representation
// Set bit 0 (RB0) to 1
portB = portB | 0x01; // OR with 00000001
// Clear bit 0
portB = portB & ~0x01; // AND with 111111101 bit = one ON/OFF state 8 bits = one byte (0 to 255) Hex is just a compact way to represent these bits: 0xFF = 11111111₂
4.2 Core bitwise operators in C
| Operator | Meaning | Typical Embedded Use |
|---|---|---|
& |
Bitwise AND | Masking (keeping some bits, clearing others). |
| |
Bitwise OR | Setting specific bits. |
^ |
Bitwise XOR | Toggling bits (useful for blinking LED). |
~ |
Bitwise NOT | Inverting bits (1 ↔ 0). |
<<, >> |
Shift left/right | Move bits into position, scaling by powers of two. |
In actual Embedded C, you often see definitions like:
#define LED_PIN (1 << 0) // Bit 0
#define RELAY_PIN (1 << 3) // Bit 3Then you use:
portB |= LED_PIN; // LED on
portB &= ~LED_PIN; // LED off
portB ^= LED_PIN; // LED toggle5. Basic Embedded I/O Ideas (Conceptual C)
Let’s think in an embedded style, but using generic C code that could be adapted to any MCU.
5.1 Digital output – LED blink (conceptual)
Suppose we have a function digitalWrite(pin, value) and delayMs(ms) provided by
our microcontroller library. A basic LED blink looks like:
void blinkLedForever(void) {
while (1) {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, 1); // LED ON
delayMs(500); // 500 ms delay
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, 0); // LED OFF
delayMs(500); // 500 ms delay
}
}You already know this style of code from your loops and functions lessons. The new idea is only: this loop is now controlling a physical LED.
5.2 Digital input – button-controlled LED
Using a hypothetical digitalRead(pin):
void buttonLedControl(void) {
while (1) {
int buttonState = digitalRead(SWITCH_PIN);
if (buttonState == 1) { // switch pressed
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, 1); // LED ON
} else {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, 0); // LED OFF
}
}
}From C side, this is just if–else. From electronics side, this is switch → microcontroller input → LED output logic.
5.3 Reading a sensor – simple threshold control
Assume we have a function analogRead(channel) that returns a 10-bit ADC value (0–1023).
void tempControl(void) {
const int THRESHOLD = 600; // example ADC value
int adcValue;
while (1) {
adcValue = analogRead(TEMP_SENSOR_CHANNEL);
if (adcValue > THRESHOLD) {
digitalWrite(FAN_RELAY_PIN, 1); // fan ON
} else {
digitalWrite(FAN_RELAY_PIN, 0); // fan OFF
}
delayMs(1000); // check once per second
}
}6. Safe C Practices for Embedded Technicians
Embedded devices are often running 24/7 in harsh environments. Bugs can cause equipment failure or unsafe behaviour. Some safe coding habits:
6.1 Use correct data types for hardware values
- Use
unsignedtypes for values that cannot be negative (e.g., ADC reading, timer counts). - Be careful with
floatin small MCUs (RAM/flash usage); prefer integer math where possible. - Know your range: if ADC is 0–1023,
unsigned intoruint16_tis fine.
6.2 Avoid slow or blocking delays in complex code
Simple projects use delayMs() loops. For more complex systems, long blocking delays make
the system unresponsive. Eventually you learn to use timers and state machines,
but at the beginning just keep delays reasonable and simple.
6.3 Always handle “else” and default cases
For example, when reading input:
if (mode == 0) {
// manual
} else if (mode == 1) {
// auto
} else {
// unknown, fail-safe mode
}In embedded systems, a safe default (e.g., turning OFF a relay in unexpected conditions) is very important.
6.4 Use named constants instead of “magic numbers”
#define TEMP_HIGH_THRESHOLD 600
#define TEMP_LOW_THRESHOLD 400This way, your code reads like a specification and can be easily modified later.
7. A Small “Embedded Style” C Module – Fan Controller
Let’s write a small, clean example that looks like Embedded C, but remains generic. Imagine an MCU that controls a fan based on temperature:
- If temperature is high → fan ON.
- If temperature is low → fan OFF.
- Use hysteresis to avoid rapid ON/OFF toggling.
#define TEMP_HIGH_THRESHOLD 600 // turn fan ON above this
#define TEMP_LOW_THRESHOLD 500 // turn fan OFF below this
void updateFanControl(void) {
static int fanState = 0; // 0 = OFF, 1 = ON
int adcValue;
adcValue = analogRead(TEMP_SENSOR_CHANNEL);
if (fanState == 0) { // currently OFF
if (adcValue > TEMP_HIGH_THRESHOLD) {
fanState = 1;
digitalWrite(FAN_RELAY_PIN, 1);
}
} else { // currently ON
if (adcValue < TEMP_LOW_THRESHOLD) {
fanState = 0;
digitalWrite(FAN_RELAY_PIN, 0);
}
}
}Then in your main loop:
int main(void) {
// init code (MCU clock, ADC, I/O, etc.) goes here
while (1) {
updateFanControl();
delayMs(1000); // check every 1 second
}
return 0;
}This is very close to how real Embedded C code looks on actual microcontrollers, only the initialization and hardware-specific function bodies change. The logic stays the same across platforms.
8. Learning Path – From Plain C to Embedded C
Many technicians ask: “Should I directly start with Arduino / STM32 / PIC, or first learn plain C?” The most effective path is usually:
- Master basic C on PC
- Write console programs (calculator, billing, mark list, mini tools).
- Practice loops,
if,switch, arrays, functions, pointers basics.
- Understand bits & bytes deeply
- Practice bitwise operators on small integers.
- Write small C programs to set, clear, toggle bits and interpret binary/hex.
- Read one microcontroller datasheet
- Learn what PORT, TRIS/DDR, ADCON, TMR registers are conceptually.
- Relate them to C variables and bit operations.
- Start with simple embedded examples
- LED blink, button, relay, sensor threshold, UART send/receive.
- Keep projects small, but practice often.
- Gradually add advanced topics
- Timers, interrupts, ADC calibration, communication protocols (UART, I²C, SPI).
- RTOS basics for more complex systems (optional, later stage).
9. Embedded-Mindset Checklist – Are You Ready?
Use this checklist to see if you are ready to move from plain C into serious Embedded C:
- I can comfortably use
if,else,switch,for,while,do-while. - I understand integer, float, char, and the difference between signed and unsigned.
- I can write small C programs that use bitwise operators to set, clear and toggle bits.
- I understand that microcontroller pins are controlled by bits in registers.
- I can imagine a loop that continuously reads inputs, applies logic, and updates outputs.
- I know how to break my program into small functions (e.g.,
readInputs(),updateOutputs()). - I am comfortable compiling and fixing basic compile-time errors and warnings in C.
FAQ: C for Electronics & Embedded Technicians
1. Do I need to master advanced C topics before starting Embedded C?
No. You don’t need advanced topics like complex pointers, dynamic memory or file handling to start basic embedded projects. But you should be comfortable with variables, conditions, loops, functions, arrays and simple pointers. You can then learn deeper C concepts as your embedded projects grow.
2. Which microcontroller should I start with for C-based embedded projects?
Any popular beginner-friendly platform is fine: Arduino (AVR / ARM), PIC, 8051, STM32, etc. The important thing is to understand concepts (I/O, ADC, timers, interrupts) rather than get stuck on one specific chip. Once you learn the pattern, switching controllers becomes easier.
3. Can I learn C only with microcontrollers, without doing PC console programs?
It’s possible, but not recommended. Debugging is harder on microcontrollers. Learning C on PC first (simple console programs) lets you focus on language concepts without hardware headaches. After that, moving to Embedded C will feel much smoother.
4. How does C compare to Arduino’s language?
Arduino “language” is basically C/C++ with a library. If you are strong in C, you can quickly understand what Arduino functions actually do under the hood, and later move beyond Arduino to raw microcontroller programming or other vendor ecosystems.
Buy link ;
Contact link ;
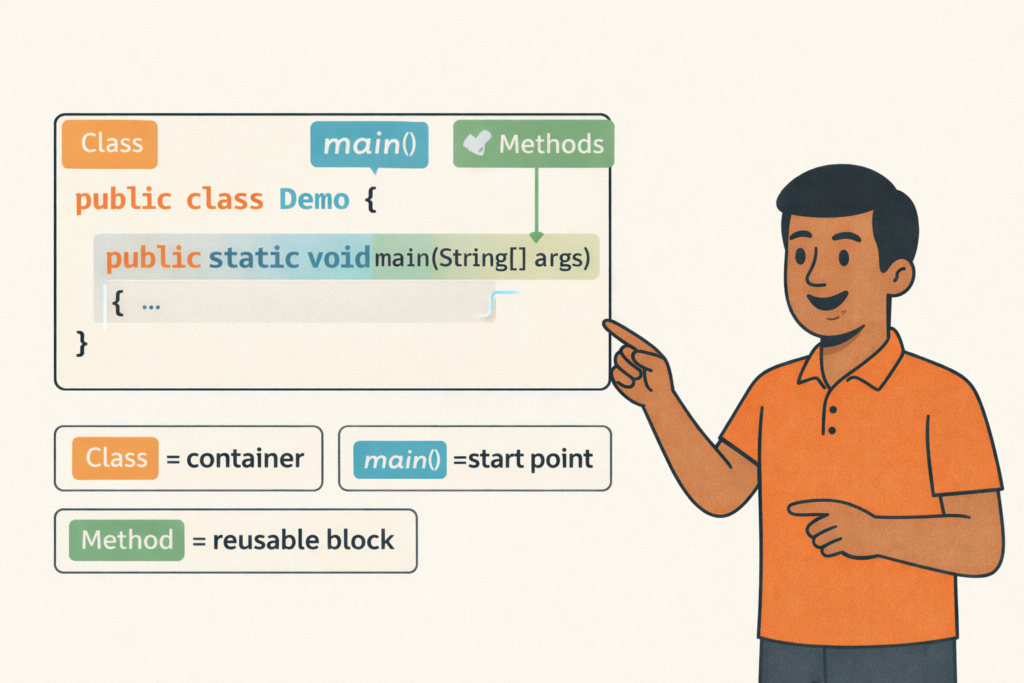
Java Program Structure (Class, main, Methods)– Full Beginner Explanation
Java Program Structure (Class, main, Methods) – Beginner Guide | Tamil Technicians TT Tamil Technicians…
Install JDK + VS Code/IntelliJ Setup+ Your First Java Program (Windows)
Install JDK + VS Code/IntelliJ Setup + First Java Program (Windows) | Tamil Technicians TT…
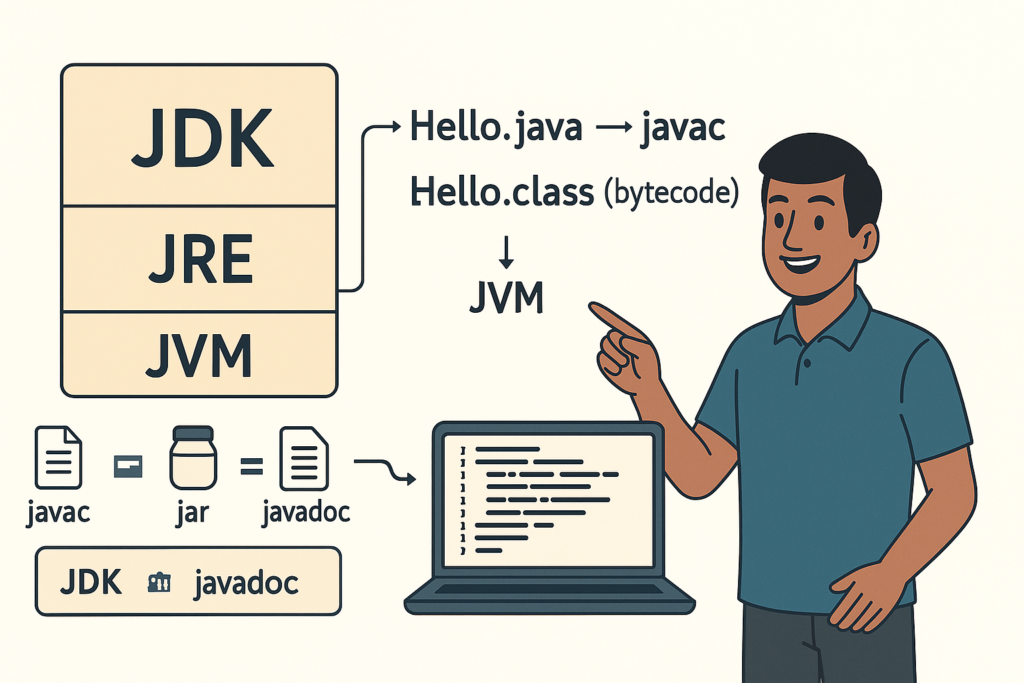
JDK vs JRE vs JVM – Easy Explanation(Compile & Run Flow for Beginners)
JDK vs JRE vs JVM – Easy Explanation (Beginner Guide) | Tamil Technicians TT Tamil…
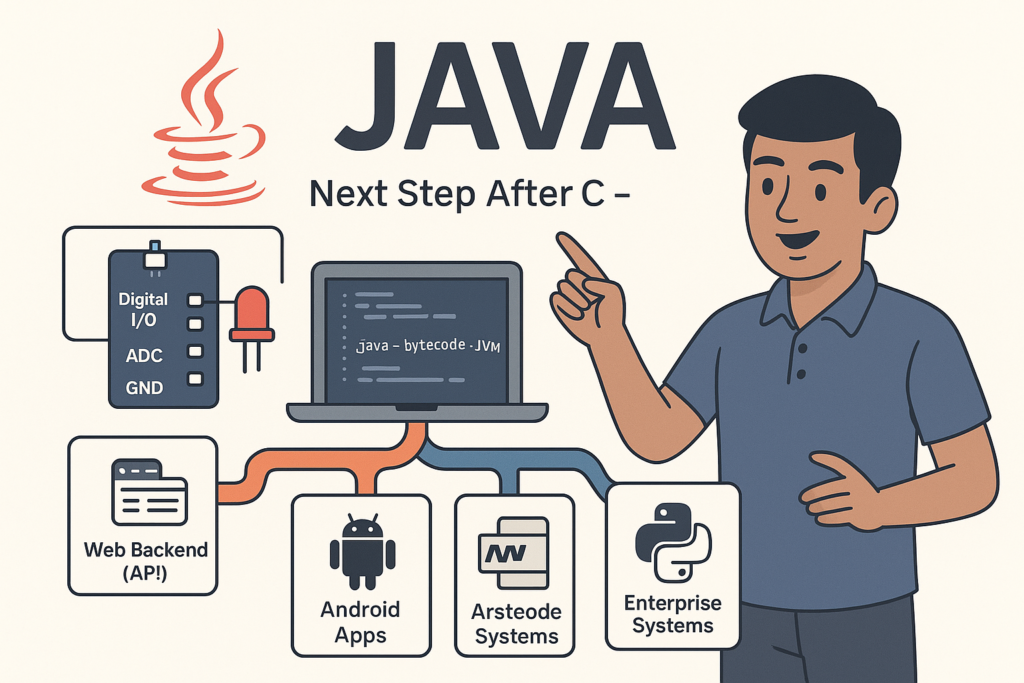
Java Introduction & Where Java is Used(Apps, Web, Banking, Android)
Java Introduction & Where Java is Used (Apps, Web, Banking, Android) | Tamil Technicians TT…
Next Step After C – What to Learn? (Embedded C, C++, Python, Linux Programming)
Next Step After C – What to Learn? (Embedded C, C++, Python, Linux Programming) |…
C for Electronics & Technicians – Basic Concepts for Embedded C
C for Electronics & Technicians – Basic Concepts for Embedded C | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
Mini C Project – Student Mark List & Result Generator in C (Console Project)
Mini C Project – Student Mark List & Result Generator in C (Console Project) |…
Mini C Projects – Simple Billing System & Calculator in C (Console Projects)
Mini C Projects – Simple Billing System & Calculator in C (Console Projects) | Tamil…
Error Types in C – Compile Time, Runtime, Logical Errors & Debugging Tips 2025
Error Types in C – Compile Time, Runtime, Logical Errors & Debugging Tips | Tamil…
Preprocessor & Macros in C – #include, #define, Conditional Compilation
Preprocessor & Macros in C – #include, #define, Conditional Compilation | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
Dynamic Memory Allocation – malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), free() Basics
Dynamic Memory Allocation in C – malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), free() Basics | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
File Handling in C – Read/Write Text Files (Sensor Log, Billing Data Examples) 2025
File Handling in C – Read/Write Text Files (Sensor Log, Billing Data Examples) | Tamil…
Storage Classes in C – auto, static, extern, register (Lifetime & Scope)
Storage Classes in C – auto, static, extern, register (Lifetime & Scope) | Tamil Technicians…
Structures in C – Struct with Examples (Student, Product, Device Data)
Structures in C – Struct with Examples (Student, Product, Device Data) | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
Pointers with Arrays, Strings & Functions – Real Use Cases
Pointers with Arrays, Strings & Functions – Real Use Cases | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
Pointers in C – Step-by-Step Visual Explanation for Beginners
Pointers in C – Step-by-Step Visual Explanation for Beginners | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians –…
Call by Value vs Call by Reference – Simple Pointer Examples in Tamil
Call by Value vs Call by Reference – Simple Pointer Examples in Tamil | Tamil…
Functions in C – User Defined Functions, Arguments, Return Types
Functions in C – User Defined Functions, Arguments, Return Types | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
Unions & Enums in C – Where and Why to Use Them?
Unions & Enums in C – Where and Why to Use Them? | Tamil Technicians…
Strings in C – char Array, gets(), puts(), String Functions (strlen, strcpy, etc.)
Strings in C – char Array, gets(), puts(), String Functions (strlen, strcpy, etc.) | Tamil…
2D Arrays in C – Tables, Matrices & Small Mini-Projects
2D Arrays in C – Tables, Matrices & Small Mini-Projects | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
Arrays in C – 1D Array Basics with Practical Examples (Marks, Bills, Readings)
Arrays in C – 1D Array Basics with Practical Examples (Marks, Bills, Readings) | Tamil…
Break, Continue & goto in C – When to Use and When to Avoid?
Break, Continue & goto in C – When to Use and When to Avoid? |…
Loops in C – for, while, do-while Complete Guide (Patterns & Practice)
Loops in C – for, while, do-while Complete Guide (Patterns & Practice) | Tamil Technicians…
switch–case in C – Menu Programs & Real Life Examples for Technicians
switch–case in C – Menu Programs & Real Life Examples for Technicians | Tamil Technicians…
Control Statements in C – if, if-else, nested if, else-if ladder (Tamil Explanation)
Control Statements in C – if, if-else, nested if, else-if ladder (Tamil Explanation) | Tamil…
Operators in C – Arithmetic, Relational, Logical & Assignment (with Examples)
Operators in C – Arithmetic, Relational, Logical & Assignment (with Examples) | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
Input & Output in C – printf(), scanf() Step-by-Step Guide 2025
Input & Output in C – printf(), scanf() Step-by-Step Guide | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
C Variables, Data Types & Constants Explained in Simple Tamil
C Variables, Data Types & Constants Explained in Simple Tamil | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
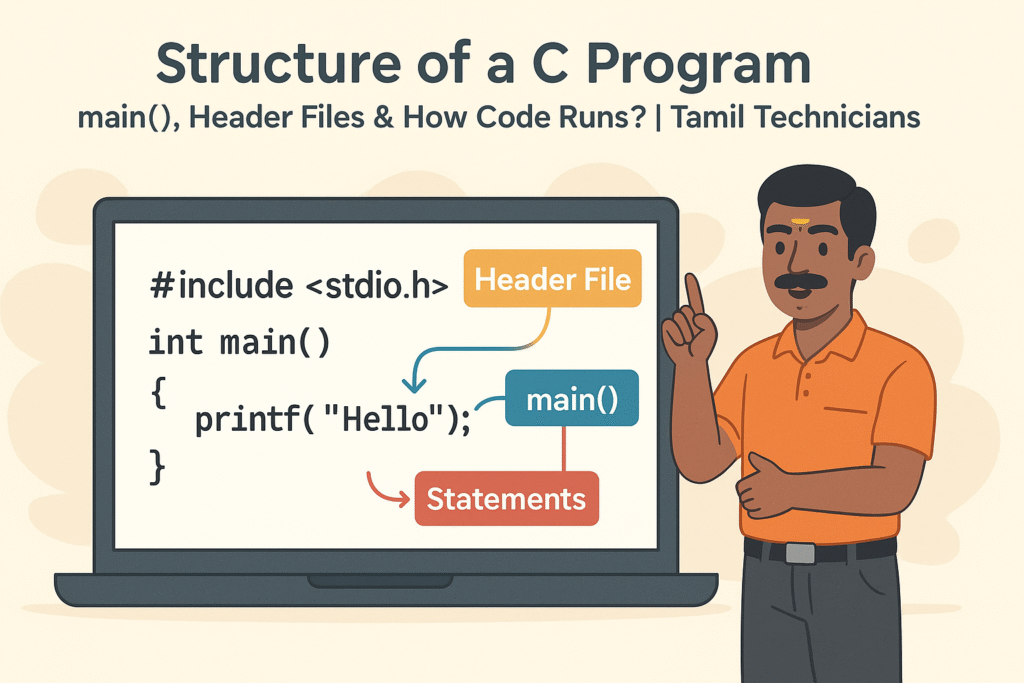
Structure of a C Program – main(), Header Files & How Code Runs?
Structure of a C Program – main(), Header Files & How Code Runs? | Tamil…
What is Programming & Why C is Important? (C Programming in Tamil for Beginners) | Tamil Technicians
What is Programming & Why C is Important? (C Programming in Tamil for Beginners) |…
C Language Introduction & Setup Guide for Beginners 2025
C Language Course Introduction & Setup Guide (Windows, Linux, macOS) | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…