Tamil Technicians – C Programming Course · Preprocessor & Macros
Preprocessor & Macros in C – #include, #define, Conditional Compilation
When you compile a C program, the compiler is not the first thing that runs. Before that,
a tool called the preprocessor processes your source code: it handles
#include, #define and conditional compilation like
#if, #ifdef, #ifndef.
In this lesson you will learn:
- What the C preprocessor does before compilation.
- How
#includeworks with header files. - How to create and use
#definemacros (constants and function-like macros). - How to use conditional compilation (
#if,#ifdef,#ifndef,#elif,#endif). - Common pitfalls with macros and best practices (when to prefer
constorinline). - Technician-style examples: debug logs, hardware configuration, building for different boards.
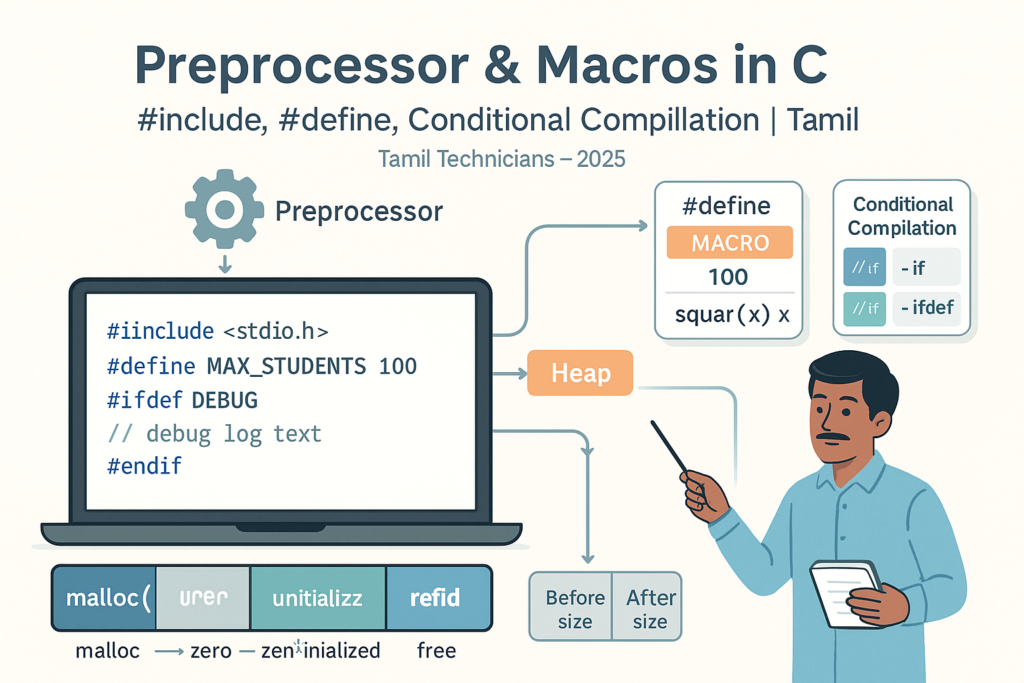
1. What Is the C Preprocessor?
The C preprocessor runs before the compiler. It reads your source code and processes
all lines starting with # (called preprocessor directives).
#include
Inserts the contents of another file (usually header files) into your source code.
#define
Defines macros: symbolic constants or code patterns which are textually substituted.
#if / #ifdef
Enables or disables parts of code depending on conditions (conditional compilation).
#undef / others
Removes macro definitions or adds special instructions to the compiler.
The preprocessor does textual substitution. It does not understand C types or semantics like the compiler does. It just follows the rules for macros and directives.
2. #include – Bringing in Declarations
You have seen lines like:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
These tell the preprocessor to copy the contents of the header files (stdio.h,
stdlib.h) into your source file at that point.
Two forms of #include
| Form | Example | Search path |
|---|---|---|
#include <...> |
#include <stdio.h> |
Searches system include directories (standard library headers). |
#include "..." |
#include "myutils.h" |
Searches current project folder first, then system paths (for user-defined headers). |
Example: user-defined header
sensor.h
#ifndef SENSOR_H
#define SENSOR_H
float read_voltage(void);
float read_current(void);
#endif // SENSOR_Hmain.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "sensor.h"
int main() {
printf("V = %.1f, I = %.2f\\n", read_voltage(), read_current());
return 0;
}
The include guard pattern (#ifndef, #define, #endif)
prevents the same header from being included multiple times in one compilation unit.
3. #define – Symbolic Constants (Object-like Macros)
The simplest use of #define is to define constants:
#define PI 3.14159
#define MAX_STUDENTS 100
#define SITE_VOLTAGE 415
Whenever the preprocessor sees PI in your code, it replaces it with 3.14159
(simple text substitution).
Technician-style example: configuration constants
#define MAX_INVERTERS 34
#define NOMINAL_AC_VOLTAGE 230.0
#define LOG_FILE "site_log.txt"Then in code:
float voltage[MAX_INVERTERS];
printf("Nominal voltage: %.1f V\\n", NOMINAL_AC_VOLTAGE);
fp = fopen(LOG_FILE, "a");const variables over #define for simple constants,
because const respects type checking and debugger visibility:
const float NOMINAL_AC_VOLTAGE = 230.0f;4. Function-like Macros – Small Inline Patterns
Macros can also take parameters (like functions), but they are still text-substitution:
#define SQUARE(x) ((x) * (x))Usage:
int a = 5;
int s = SQUARE(a + 1); // expands to ((a + 1) * (a + 1))Why use extra parentheses?
Without parentheses:
#define BAD_SQUARE(x) x * x
int s = BAD_SQUARE(a + 1); // becomes a + 1 * a + 1 (wrong)
Using ((x) * (x)) ensures correct order of operations.
Technician-style macro examples
#define VOLT_TO_KW(v, i) ((v) * (i) / 1000.0f)
#define IS_OVER_LIMIT(v, limit) ((v) > (limit))In code:
float v = 230.0f, i = 12.5f;
float power = VOLT_TO_KW(v, i); // 2.875 kW approx
if (IS_OVER_LIMIT(v, NOMINAL_AC_VOLTAGE + 10.0f)) {
printf("Voltage over limit!\\n");
}inline functions (in C99 and later).
5. Macro Pitfalls & Best Practices
| Pitfall | Example | Safer version |
|---|---|---|
| Missing parentheses | #define MUL(a,b) a*b |
#define MUL(a,b) ((a)*(b)) |
| Side effects in arguments | #define SQR(x) ((x)*(x)) |
Don’t pass expressions with ++/-- into macros. |
| No type checking | #define ADD(a,b) ((a)+(b)) |
Use real functions if types matter. |
| Unexpected scope | Macros are global once defined. | Use #undef or limit usage region. |
- Use ALL_CAPS names for macros to distinguish them from variables and functions.
- Add parentheses around macro parameters and the whole macro expression.
- Prefer
constvariables andinlinefunctions for complex logic. - Use macros mainly for: constants, small simple expressions, conditional compilation flags.
6. Conditional Compilation – #if, #ifdef, #ifndef, #elif, #endif
Conditional compilation lets you enable or disable blocks of code at compile time based on conditions. This is extremely useful for:
- Debug vs release builds (extra logs, assertions).
- Different hardware boards or sites.
- Enabling or disabling experimental features.
Basic forms
#if condition
// code
#elif other_condition
// other code
#else
// fallback
#endif#ifdef MACRO_NAME
// code if MACRO_NAME is defined
#endif
#ifndef MACRO_NAME
// code if MACRO_NAME is NOT defined
#endifExample: debug logging macro
#define DEBUG // comment this line to disable debug
#ifdef DEBUG
#define LOG(msg) printf("DEBUG: %s\\n", msg)
#else
#define LOG(msg) // expands to nothing
#endif
int main() {
LOG("Program started");
// ...
LOG("Program finished");
return 0;
}
If DEBUG is defined, LOG("...") prints messages. If not, the macro expands to
nothing and the debug code is removed from the compiled binary.
Technician-style example: site configuration
#define SITE_A
// #define SITE_B
#ifdef SITE_A
#define SITE_NAME "Nandhavanapatti"
#define MAX_MW 10
#elif defined(SITE_B)
#define SITE_NAME "Another Solar Site"
#define MAX_MW 5
#else
#define SITE_NAME "Unknown Site"
#define MAX_MW 1
#endif
printf("Running config for %s (%d MW)\\n", SITE_NAME, MAX_MW);7. Header Guards & #pragma once
If a header file is included multiple times (directly or indirectly), you can get duplicate-definition errors. To prevent this, we use header guards.
Standard pattern (portable)
#ifndef CONFIG_H
#define CONFIG_H
#define FW_VERSION "1.0.3"
#define MAX_INVERTERS 34
#endif // CONFIG_H
Here, if CONFIG_H is not yet defined, the block is included and CONFIG_H is defined.
On subsequent includes, CONFIG_H is already defined so the content is skipped.
#pragma once (non-standard but common)
#pragma once
#define FW_VERSION "1.0.3"
#define MAX_INVERTERS 34
#pragma once tells the compiler to include the file only once.
It is widely supported but not part of the C standard; header guards are fully portable.
8. #undef and Other Useful Directives
#undef – Cancel a Macro
#define TEMP_LIMIT 60
// ... some code
#undef TEMP_LIMIT // macro is no longer defined here
After #undef TEMP_LIMIT, the name TEMP_LIMIT no longer expands as a macro.
#error – Generate a Compile-Time Error
#ifndef SITE_NAME
#error "SITE_NAME is not defined! Please set site configuration."
#endifThis is useful to catch missing configuration at compile time instead of discovering it in runtime.
9. Real Use Cases – Technicians & Embedded C Style
9.1 Board-specific code
#define BOARD_V1
// #define BOARD_V2
#ifdef BOARD_V1
#define RELAY_PIN 5
#elif defined(BOARD_V2)
#define RELAY_PIN 12
#else
#define RELAY_PIN 0
#endif
Now the rest of the code can use RELAY_PIN without if–else everywhere.
9.2 Enabling extra diagnostics only in development builds
#ifdef DEBUG
#define DIAG_PRINT(fmt, ...) \
printf("DIAG: " fmt "\\n", ##__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define DIAG_PRINT(fmt, ...) // nothing
#endif
In production, you simply compile without DEBUG defined and your binaries are smaller and faster.
10. Learning Checklist – Preprocessor & Macros
- I know that the preprocessor runs before the actual C compilation.
- I understand how
#includebrings in declarations from header files. - I can use
#definefor symbolic constants and simple macros. - I know the difference between object-like macros and function-like macros.
- I can write safe macros with proper parentheses and without side-effect arguments.
- I can use
#if,#ifdef,#ifndef,#elif,#endiffor conditional compilation. - I know how header guards work and why they are important.
- I understand when to prefer
constor functions instead of complex macros.
FAQ: Preprocessor & Macros in C
1. Is the preprocessor part of the C compiler?
It is usually implemented as a separate step before compilation, although many modern compilers
integrate it internally. Conceptually, it is a distinct phase that processes directives like
#include and #define before normal C compilation begins.
2. When should I use macros instead of functions?
Macros are useful for simple constants, small inline expressions, and conditional compilation flags.
For most calculations and logic, real functions (possibly marked inline) are safer because
they have type checking, proper scoping and easier debugging.
3. Why do we need header guards?
Without header guards, including the same header multiple times can lead to duplicate declarations and definitions, causing compilation errors. Header guards ensure that a header’s contents are only included once in each translation unit.
4. What is the difference between #ifdef and #if defined()?
#ifdef MACRO is shorthand for #if defined(MACRO). Both check whether a macro
is defined. #if defined(MACRO) || defined(OTHER) is more flexible when combining multiple
conditions, but #ifdef is convenient for simple single-macro checks.
Buy link ;
Cantact link ;
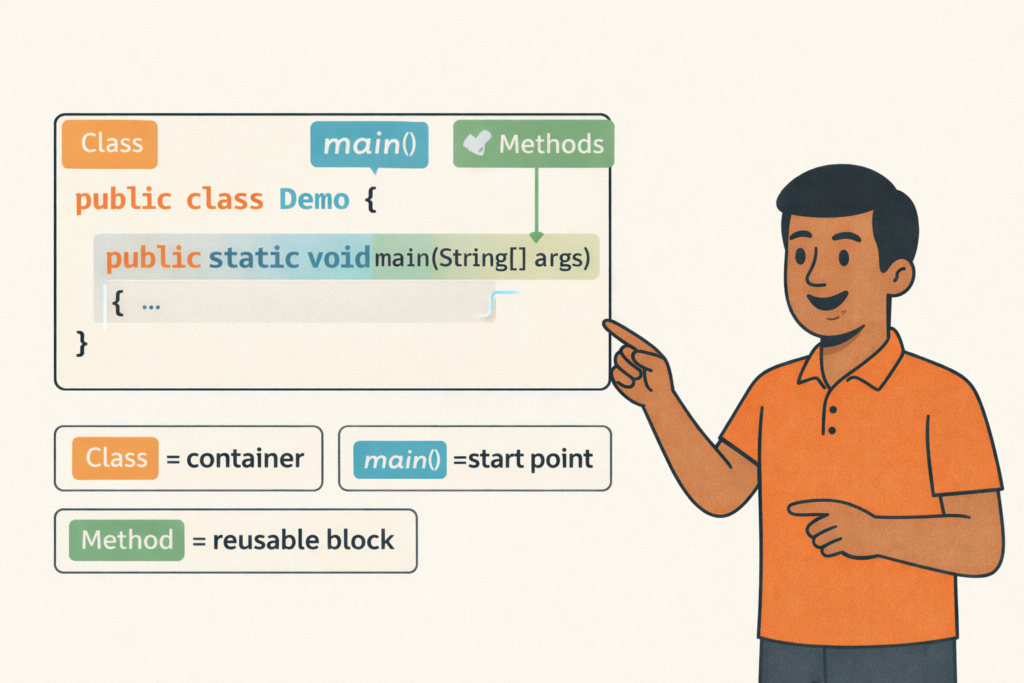
Java Program Structure (Class, main, Methods)– Full Beginner Explanation
Java Program Structure (Class, main, Methods) – Beginner Guide | Tamil Technicians TT Tamil Technicians…
Install JDK + VS Code/IntelliJ Setup+ Your First Java Program (Windows)
Install JDK + VS Code/IntelliJ Setup + First Java Program (Windows) | Tamil Technicians TT…
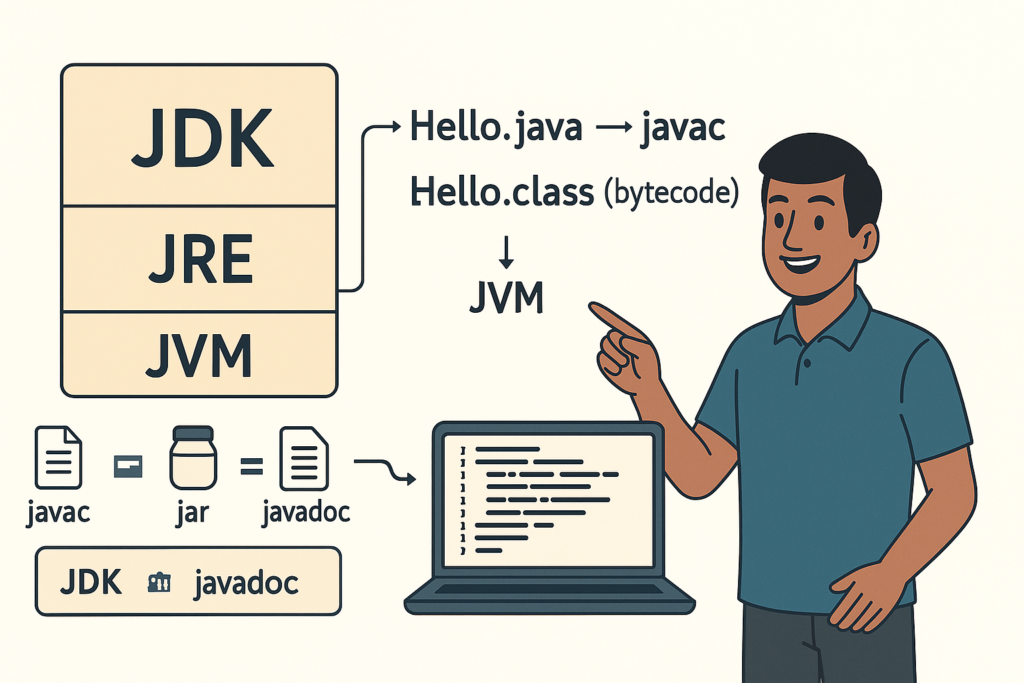
JDK vs JRE vs JVM – Easy Explanation(Compile & Run Flow for Beginners)
JDK vs JRE vs JVM – Easy Explanation (Beginner Guide) | Tamil Technicians TT Tamil…
Java Introduction & Where Java is Used(Apps, Web, Banking, Android)
Java Introduction & Where Java is Used (Apps, Web, Banking, Android) | Tamil Technicians TT…
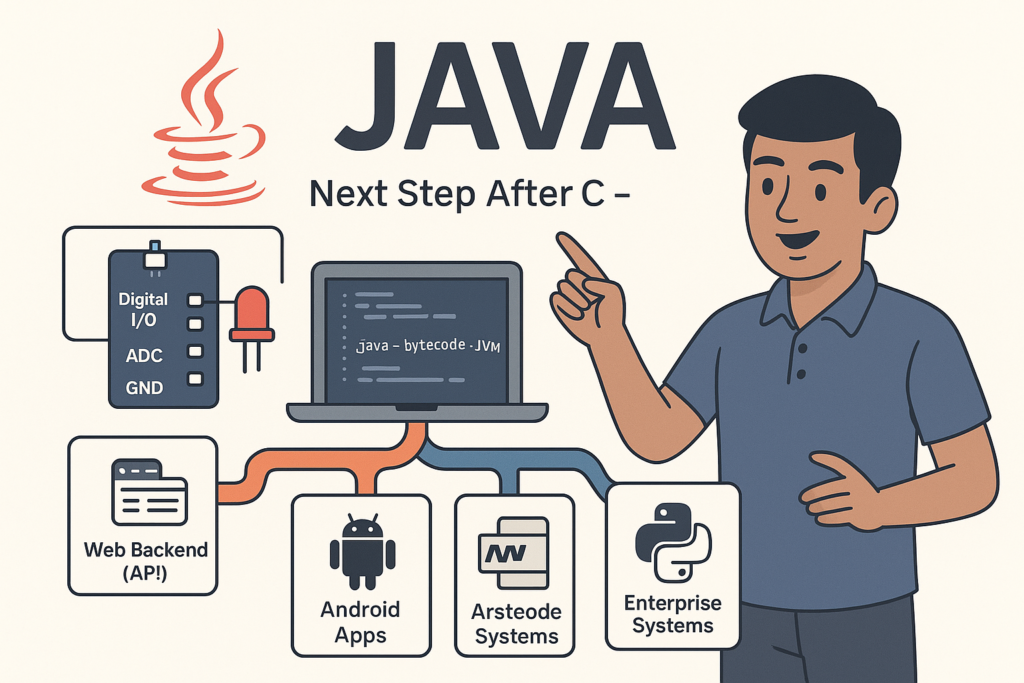
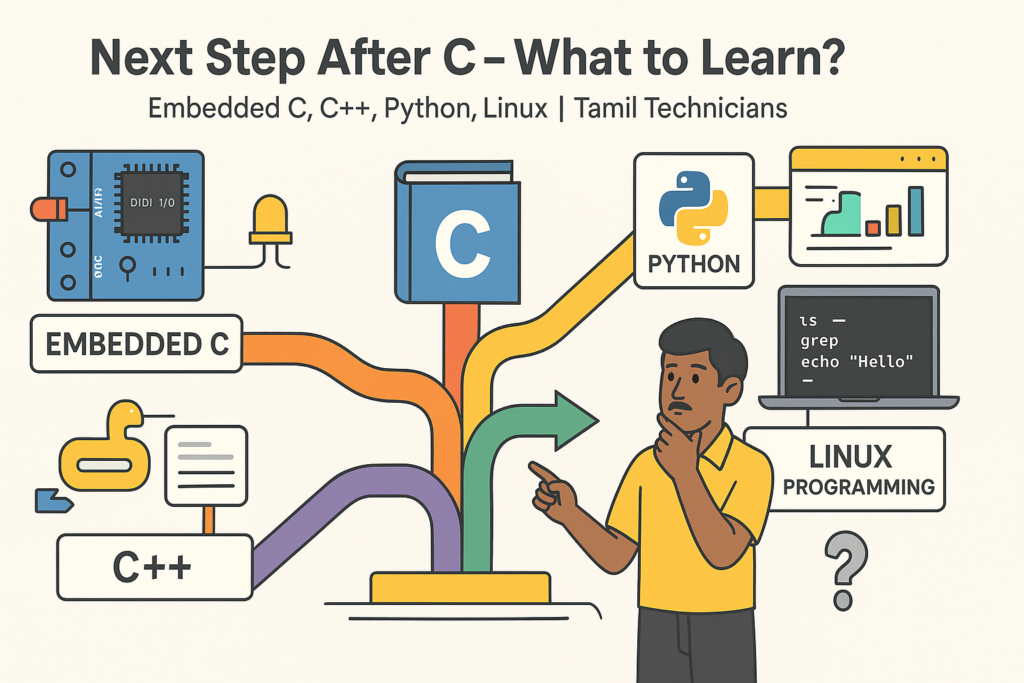
Next Step After C – What to Learn? (Embedded C, C++, Python, Linux Programming)
Next Step After C – What to Learn? (Embedded C, C++, Python, Linux Programming) |…
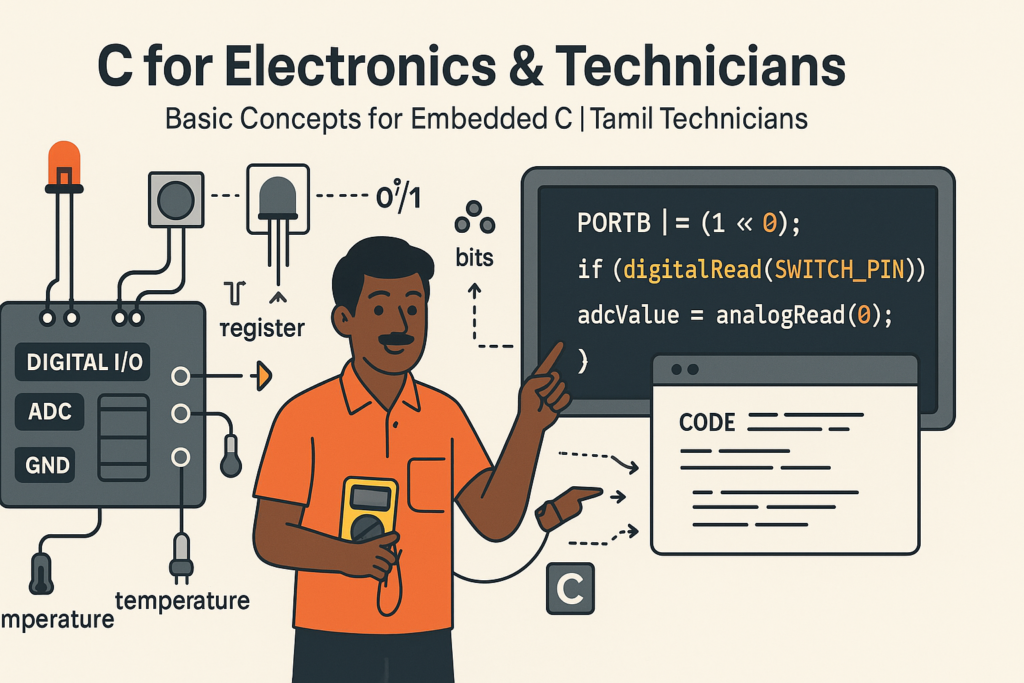
C for Electronics & Technicians – Basic Concepts for Embedded C
C for Electronics & Technicians – Basic Concepts for Embedded C | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
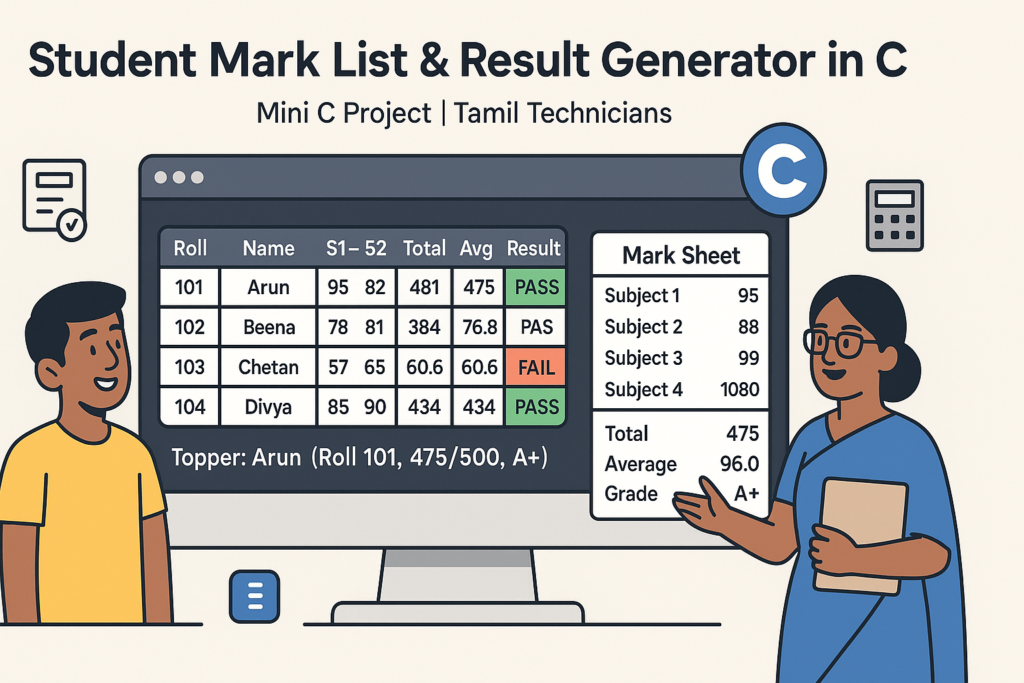
Mini C Project – Student Mark List & Result Generator in C (Console Project)
Mini C Project – Student Mark List & Result Generator in C (Console Project) |…
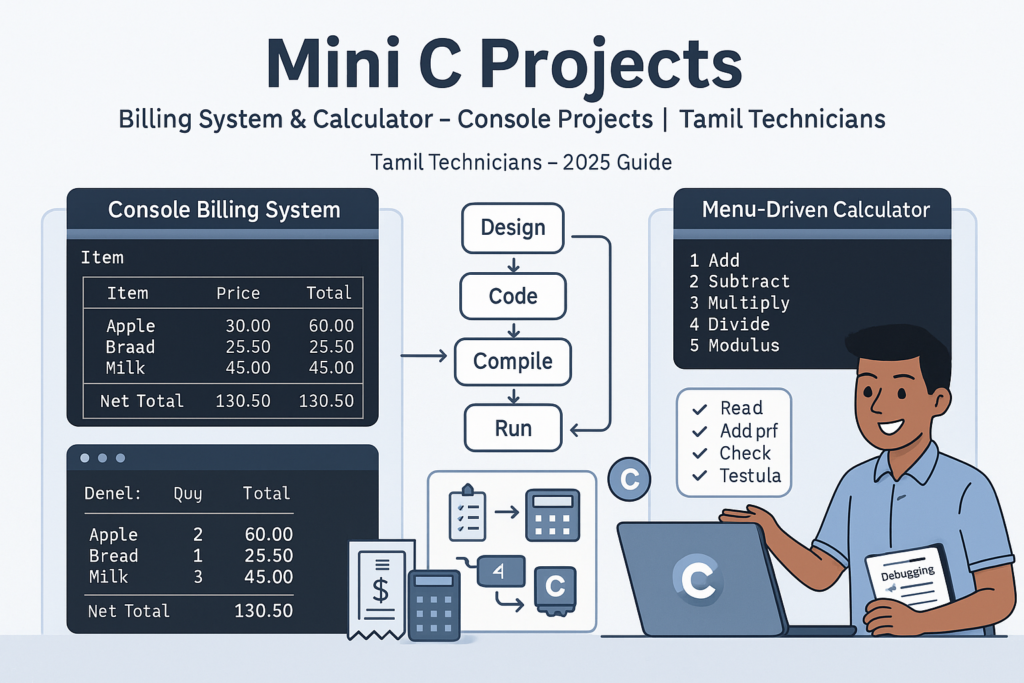
Mini C Projects – Simple Billing System & Calculator in C (Console Projects)
Mini C Projects – Simple Billing System & Calculator in C (Console Projects) | Tamil…
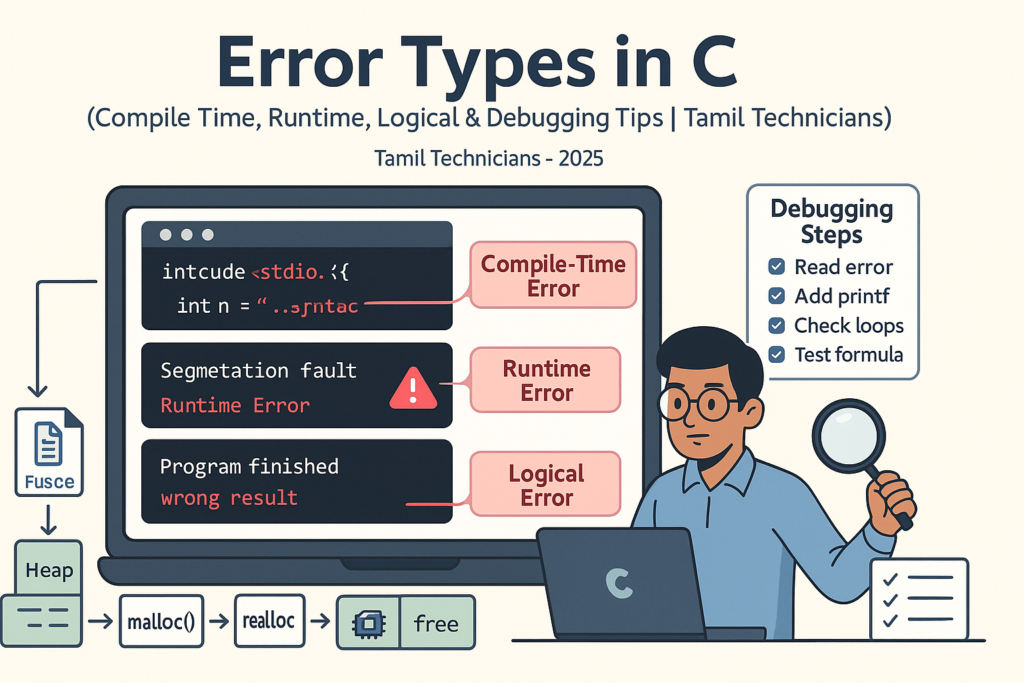
Error Types in C – Compile Time, Runtime, Logical Errors & Debugging Tips 2025
Error Types in C – Compile Time, Runtime, Logical Errors & Debugging Tips | Tamil…
Preprocessor & Macros in C – #include, #define, Conditional Compilation
Preprocessor & Macros in C – #include, #define, Conditional Compilation | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
Dynamic Memory Allocation – malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), free() Basics
Dynamic Memory Allocation in C – malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), free() Basics | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
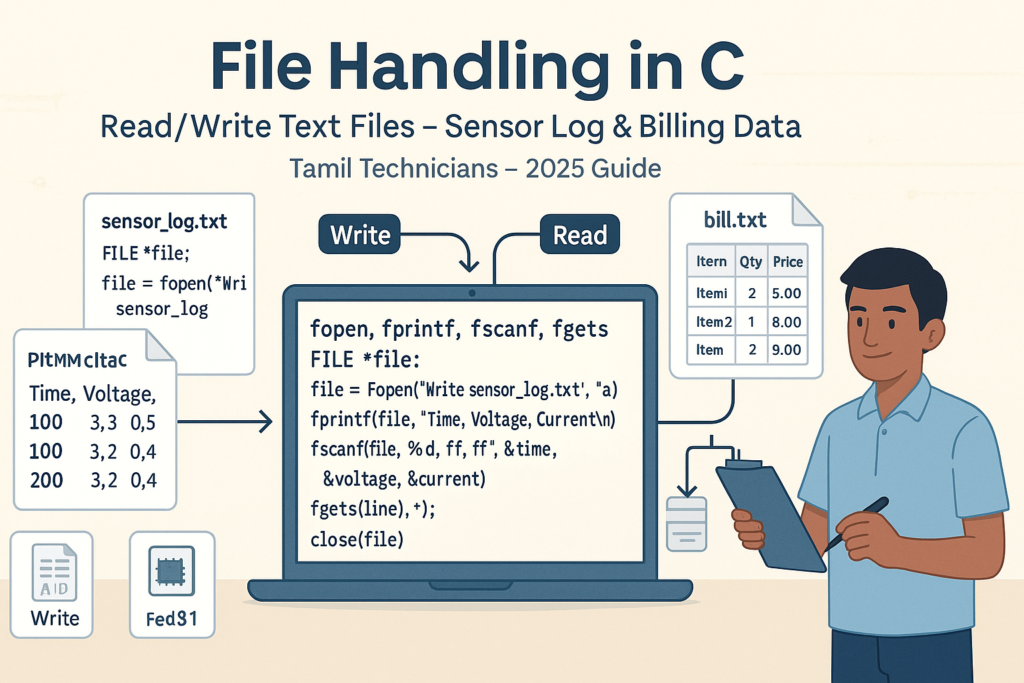
File Handling in C – Read/Write Text Files (Sensor Log, Billing Data Examples) 2025
File Handling in C – Read/Write Text Files (Sensor Log, Billing Data Examples) | Tamil…
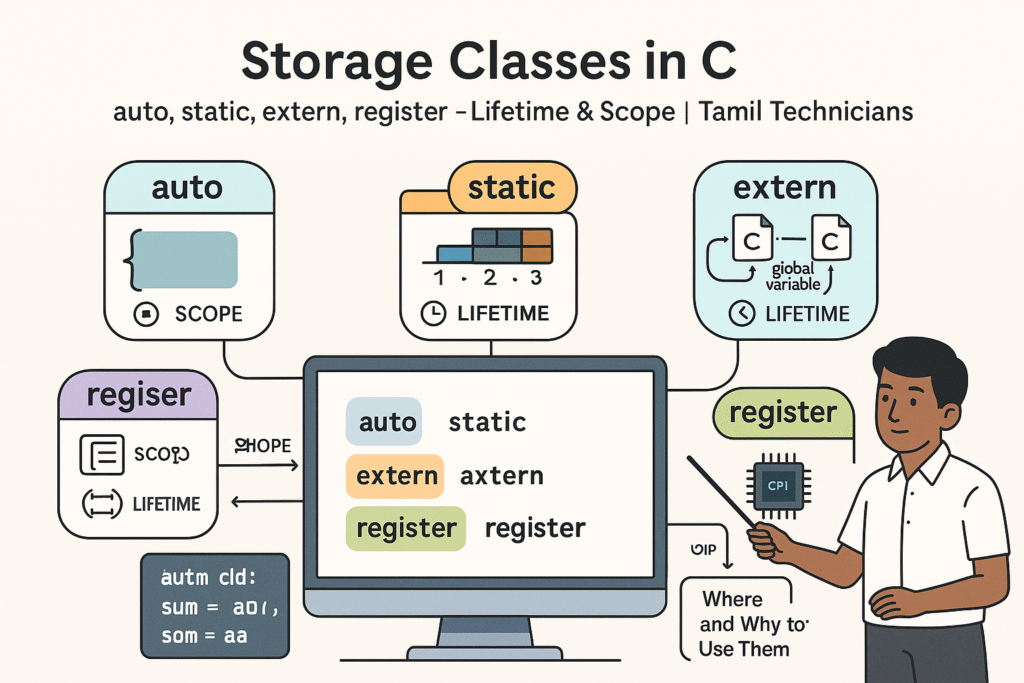
Storage Classes in C – auto, static, extern, register (Lifetime & Scope)
Storage Classes in C – auto, static, extern, register (Lifetime & Scope) | Tamil Technicians…
Structures in C – Struct with Examples (Student, Product, Device Data)
Structures in C – Struct with Examples (Student, Product, Device Data) | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
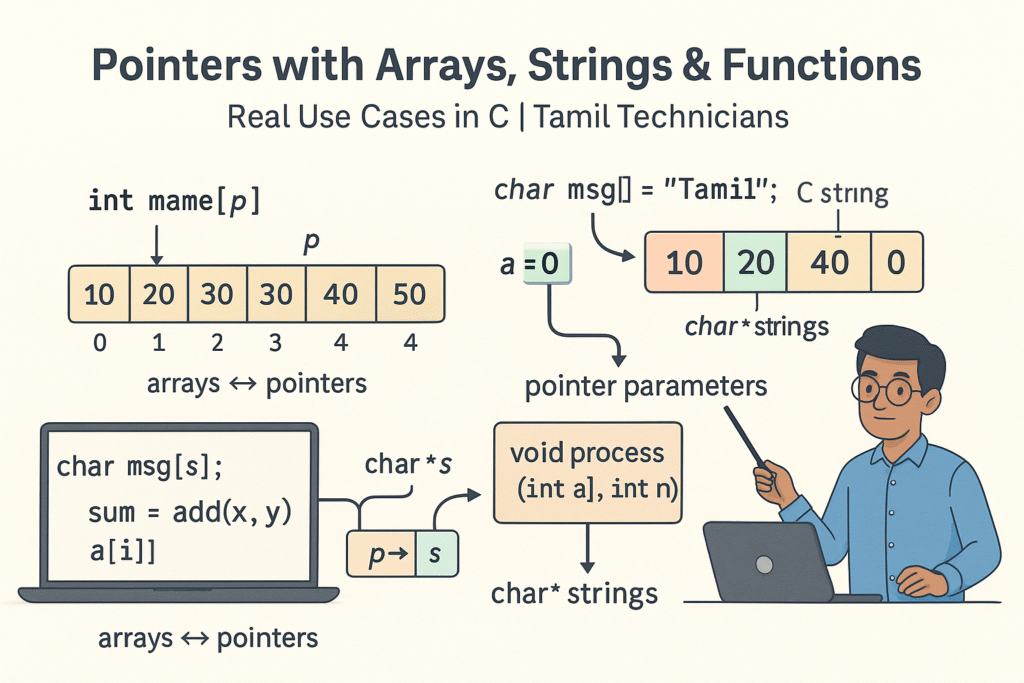
Pointers with Arrays, Strings & Functions – Real Use Cases
Pointers with Arrays, Strings & Functions – Real Use Cases | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
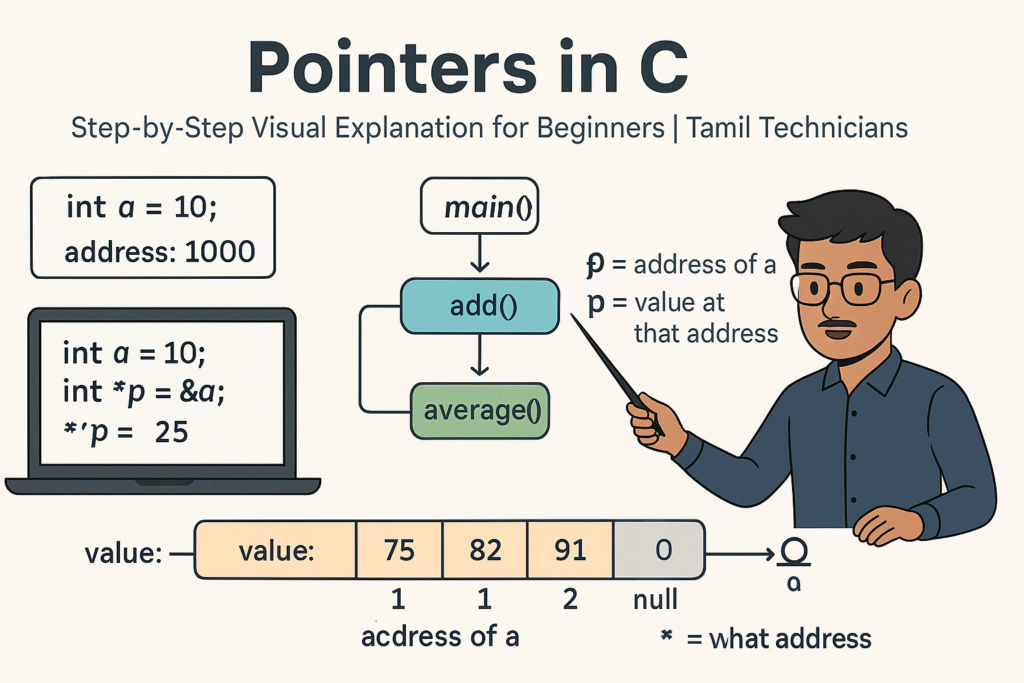
Pointers in C – Step-by-Step Visual Explanation for Beginners
Pointers in C – Step-by-Step Visual Explanation for Beginners | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians –…
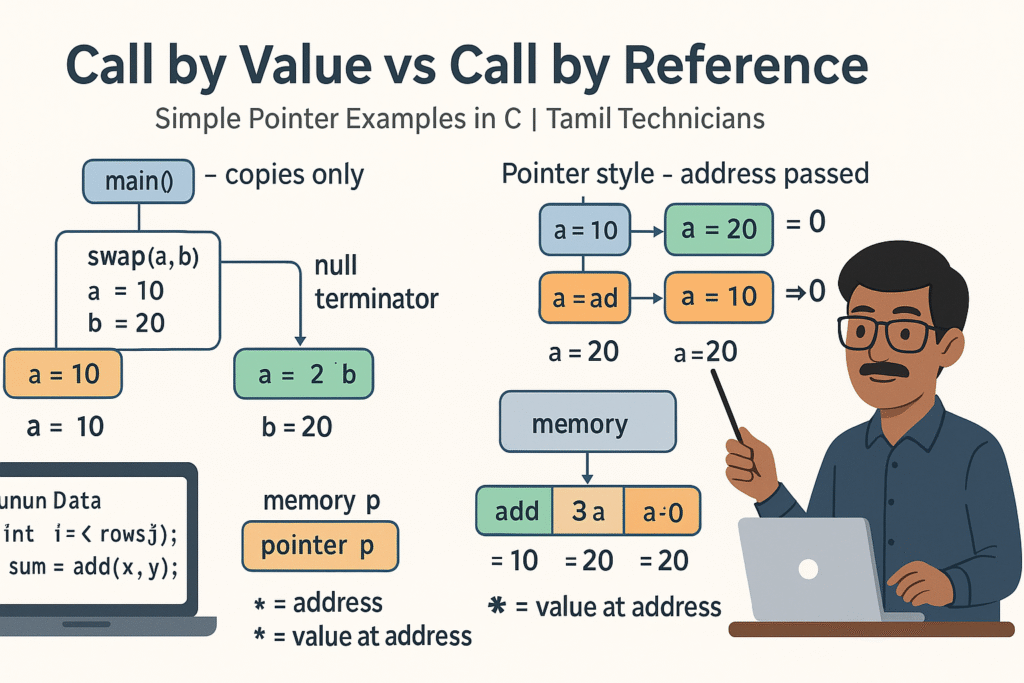
Call by Value vs Call by Reference – Simple Pointer Examples in Tamil
Call by Value vs Call by Reference – Simple Pointer Examples in Tamil | Tamil…
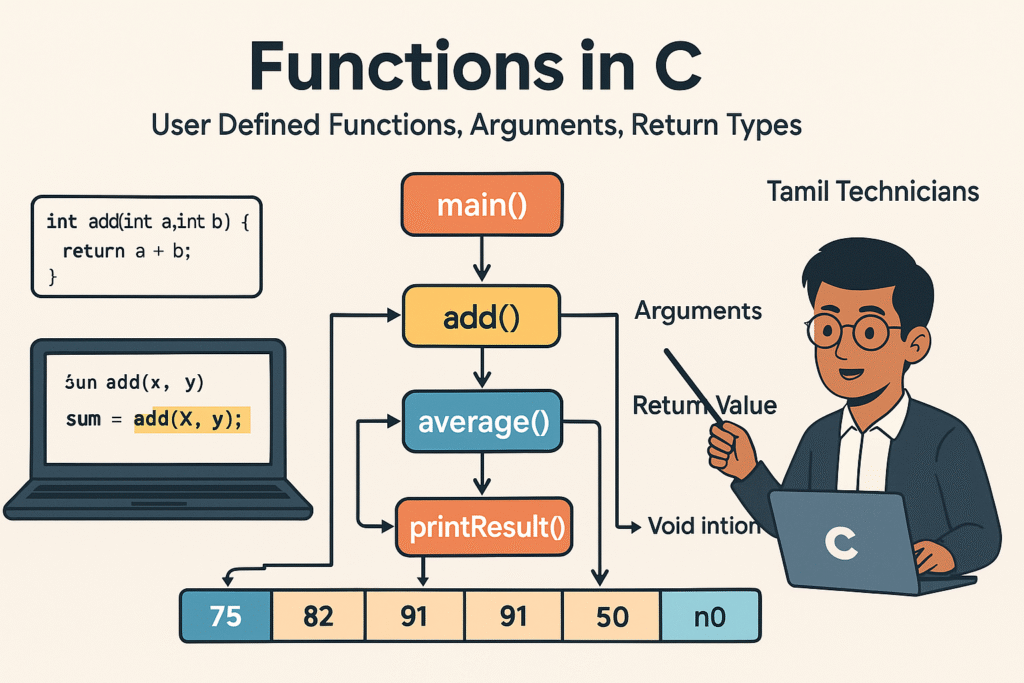
Functions in C – User Defined Functions, Arguments, Return Types
Functions in C – User Defined Functions, Arguments, Return Types | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
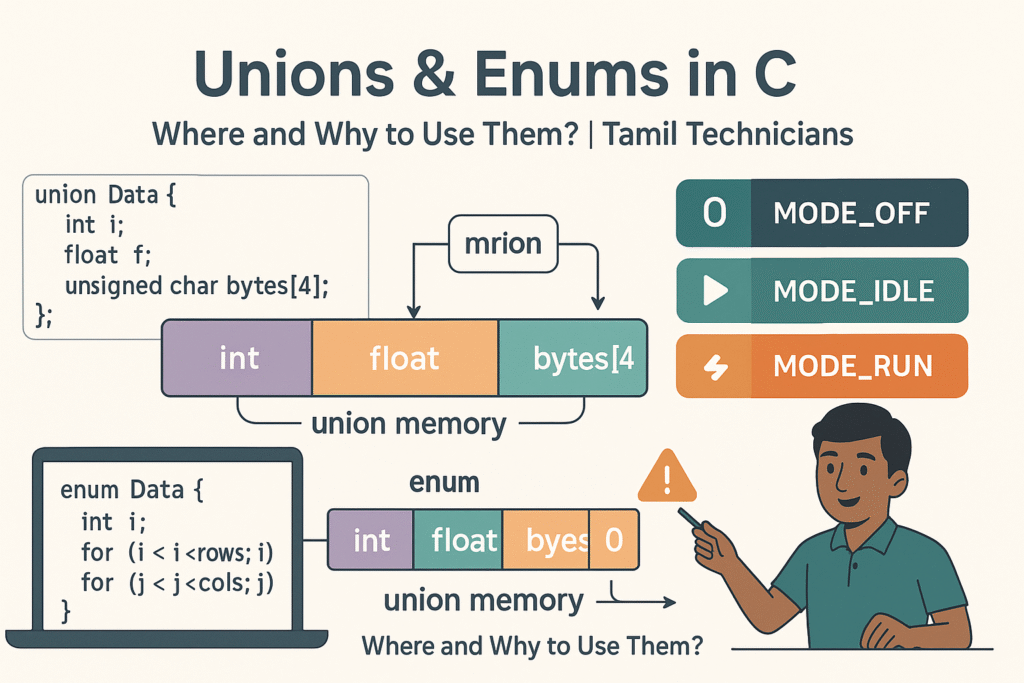
Unions & Enums in C – Where and Why to Use Them?
Unions & Enums in C – Where and Why to Use Them? | Tamil Technicians…
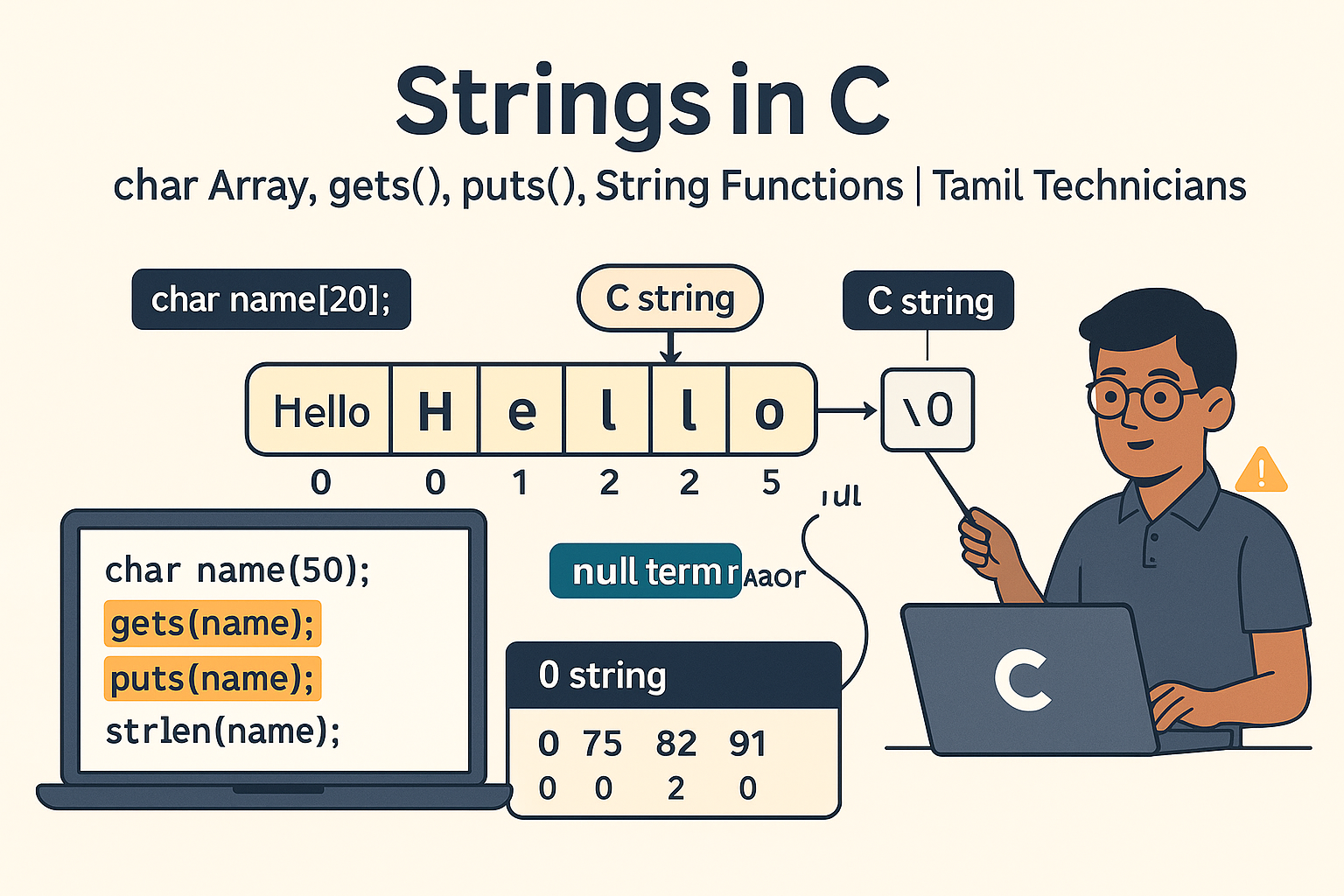
Strings in C – char Array, gets(), puts(), String Functions (strlen, strcpy, etc.)
Strings in C – char Array, gets(), puts(), String Functions (strlen, strcpy, etc.) | Tamil…
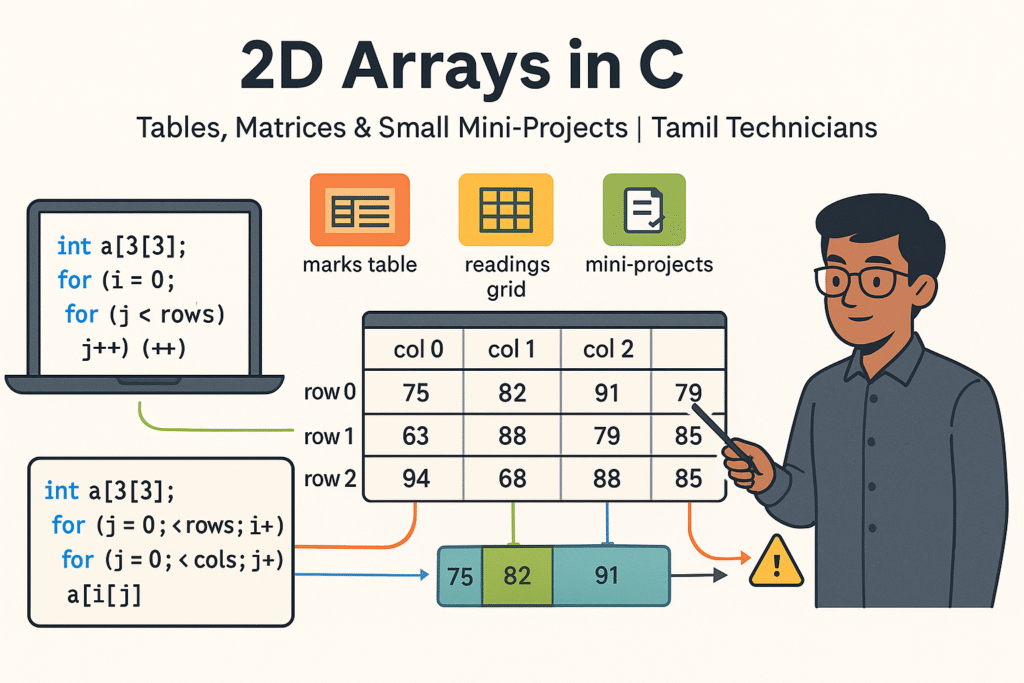
2D Arrays in C – Tables, Matrices & Small Mini-Projects
2D Arrays in C – Tables, Matrices & Small Mini-Projects | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
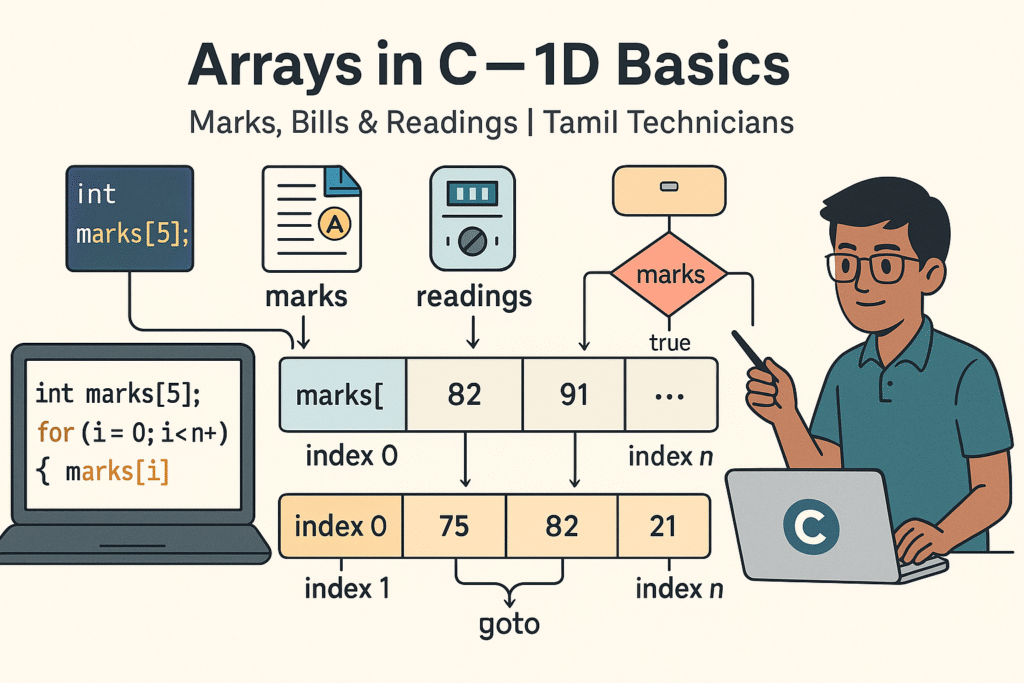
Arrays in C – 1D Array Basics with Practical Examples (Marks, Bills, Readings)
Arrays in C – 1D Array Basics with Practical Examples (Marks, Bills, Readings) | Tamil…
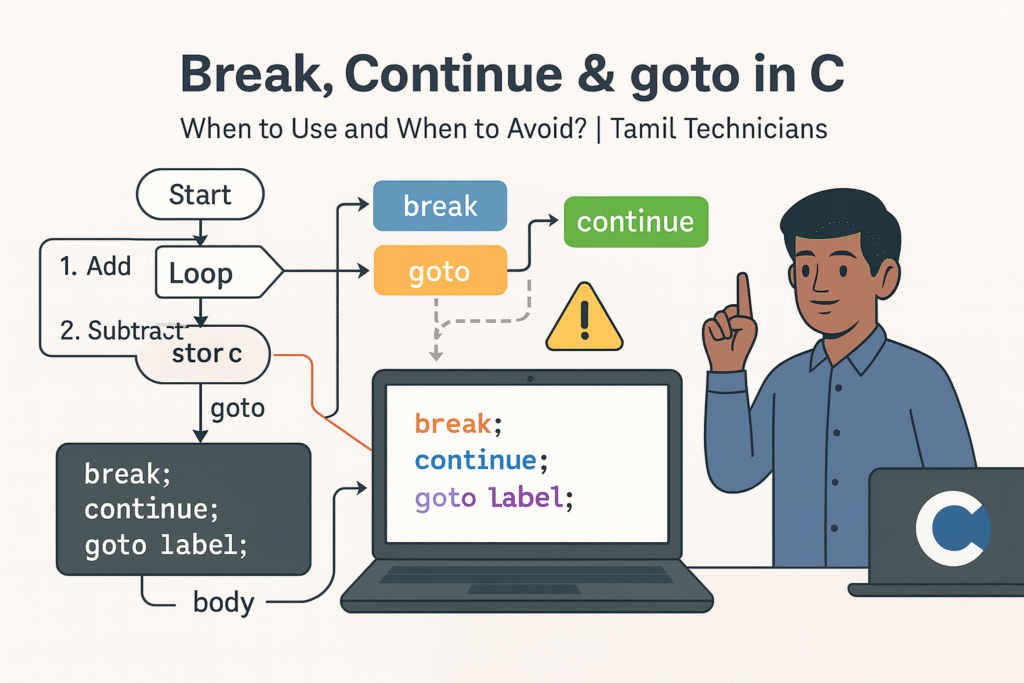
Break, Continue & goto in C – When to Use and When to Avoid?
Break, Continue & goto in C – When to Use and When to Avoid? |…
Loops in C – for, while, do-while Complete Guide (Patterns & Practice)
Loops in C – for, while, do-while Complete Guide (Patterns & Practice) | Tamil Technicians…
switch–case in C – Menu Programs & Real Life Examples for Technicians
switch–case in C – Menu Programs & Real Life Examples for Technicians | Tamil Technicians…
Control Statements in C – if, if-else, nested if, else-if ladder (Tamil Explanation)
Control Statements in C – if, if-else, nested if, else-if ladder (Tamil Explanation) | Tamil…
Operators in C – Arithmetic, Relational, Logical & Assignment (with Examples)
Operators in C – Arithmetic, Relational, Logical & Assignment (with Examples) | Tamil Technicians Tamil…
Input & Output in C – printf(), scanf() Step-by-Step Guide 2025
Input & Output in C – printf(), scanf() Step-by-Step Guide | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
C Variables, Data Types & Constants Explained in Simple Tamil
C Variables, Data Types & Constants Explained in Simple Tamil | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…
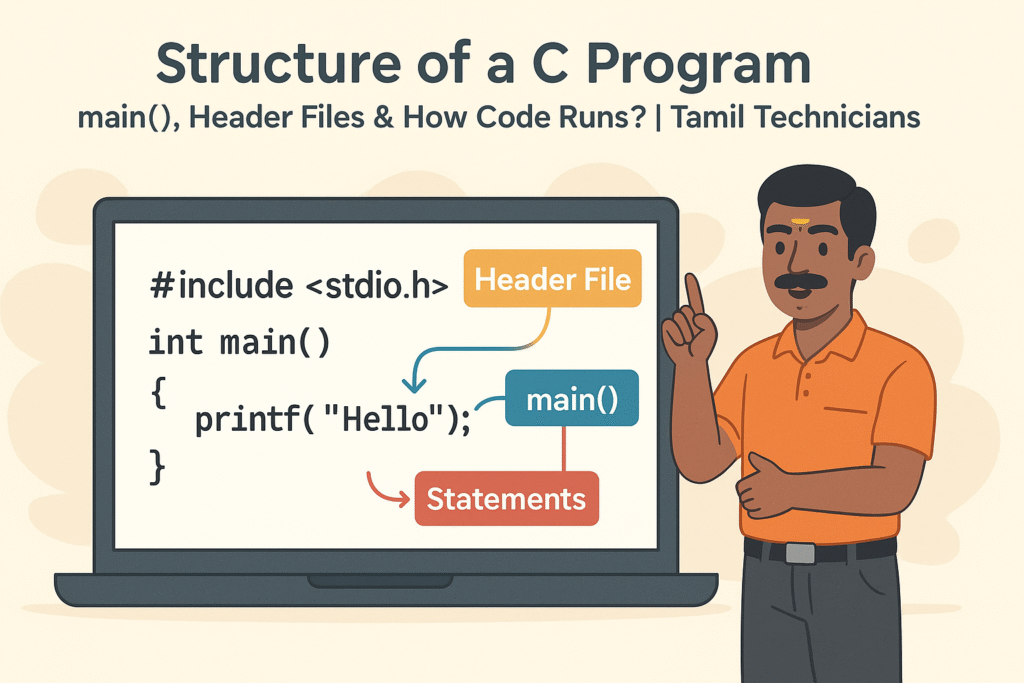
Structure of a C Program – main(), Header Files & How Code Runs?
Structure of a C Program – main(), Header Files & How Code Runs? | Tamil…
What is Programming & Why C is Important? (C Programming in Tamil for Beginners) | Tamil Technicians
What is Programming & Why C is Important? (C Programming in Tamil for Beginners) |…
C Language Introduction & Setup Guide for Beginners 2025
C Language Course Introduction & Setup Guide (Windows, Linux, macOS) | Tamil Technicians Tamil Technicians…